Growth and Mortality Outcomes for Different Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation Criteria in Children Ages 1-5 Years: A Causal Modeling Analysis
- PMID: 26479876
- PMCID: PMC5410645
- DOI: 10.1097/EDE.0000000000000412
Growth and Mortality Outcomes for Different Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation Criteria in Children Ages 1-5 Years: A Causal Modeling Analysis
Abstract
Background: There is limited evidence regarding the optimal timing of initiating antiretroviral therapy (ART) in children. We conducted a causal modeling analysis in children ages 1-5 years from the International Epidemiologic Databases to Evaluate AIDS West/Southern-Africa collaboration to determine growth and mortality differences related to different CD4-based treatment initiation criteria, age groups, and regions.
Methods: ART-naïve children of ages 12-59 months at enrollment with at least one visit before ART initiation and one follow-up visit were included. We estimated 3-year growth and cumulative mortality from the start of follow-up for different CD4 criteria using g-computation.
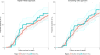
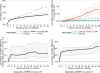
Results: About one quarter of the 5,826 included children was from West Africa (24.6%).The median (first; third quartile) CD4% at the first visit was 16% (11%; 23%), the median weight-for-age z-scores and height-for-age z-scores were -1.5 (-2.7; -0.6) and -2.5 (-3.5; -1.5), respectively. Estimated cumulative mortality was higher overall, and growth was slower, when initiating ART at lower CD4 thresholds. After 3 years of follow-up, the estimated mortality difference between starting ART routinely irrespective of CD4 count and starting ART if either CD4 count <750 cells/mm³ or CD4% <25% was 0.2% (95% CI = -0.2%; 0.3%), and the difference in the mean height-for-age z-scores of those who survived was -0.02 (95% CI = -0.04; 0.01). Younger children ages 1-2 and children in West Africa had worse outcomes.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that earlier treatment initiation yields overall better growth and mortality outcomes, although we could not show any differences in outcomes between immediate ART and delaying until CD4 count/% falls below 750/25%.
Conflict of interest statement
The National Institutes of Health, WHO, NIAID, NCI, and NICHD had no role in data collection and analysis, decision to publish, and preparation of the manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- UNAIDS. Report on the global AIDS epidemic 2013. Geneva: 2013.
-
- Puthanakit T, Bunupuradah T. Early versus deferred antiretroviral therapy in children in low-income and middle-income countries. Current Opinions in HIV/AIDS. 2010;5(1):12–17. - PubMed
-
- Turkova A, Webb RH, Lyall H. When to start, what to start and other treatment controversies in pediatric HIV infection. Paediatr Drugs. 2012;14(6):361–376. - PubMed

