Hair follicle-derived IL-7 and IL-15 mediate skin-resident memory T cell homeostasis and lymphoma
- PMID: 26479922
- PMCID: PMC4636445
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3962
Hair follicle-derived IL-7 and IL-15 mediate skin-resident memory T cell homeostasis and lymphoma
Abstract
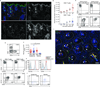
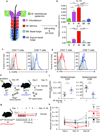
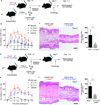
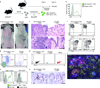
The skin harbors a variety of resident leukocyte subsets that must be tightly regulated to maintain immune homeostasis. Hair follicles are unique structures in the skin that contribute to skin dendritic cell homeostasis through chemokine production. We demonstrate that CD4(+) and CD8(+) skin-resident memory T cells (TRM cells), which are responsible for long-term skin immunity, reside predominantly within the hair follicle epithelium of the unperturbed epidermis. TRM cell tropism for the epidermis and follicles is herein termed epidermotropism. Hair follicle expression of IL-15 was required for CD8(+) TRM cells, and IL-7 for CD8(+) and CD4(+) TRM cells, to exert epidermotropism. A lack of either cytokine in the skin led to impaired hapten-induced contact hypersensitivity responses. In a model of cutaneous T cell lymphoma, epidermotropic CD4(+) TRM lymphoma cell localization depended on the presence of hair follicle-derived IL-7. These findings implicate hair follicle-derived cytokines as regulators of malignant and non-malignant TRM cell tissue residence, and they suggest that the cytokines may be targeted therapeutically in inflammatory skin diseases and lymphoma.
Figures

References
-
- Cotsarelis G, Sun TT, Lavker RM. Label-retaining cells reside in the bulge area of pilosebaceous unit: implications for follicular stem cells, hair cycle, and skin carcinogenesis. Cell. 1990;61:1329–1337. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura EK, et al. Dominant role of the niche in melanocyte stem-cell fate determination. Nature. 2002;416:854–860. - PubMed
-
- Christoph T, et al. The human hair follicle immune system: cellular composition and immune privilege. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:862–873. - PubMed
-
- Clark RA, et al. The vast majority of CLA+ T cells are resident in normal skin. J Immunol. 2006;176:4431–4439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

