Erythropoietin Stimulates Tumor Growth via EphB4
- PMID: 26481148
- PMCID: PMC4643364
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.09.008
Erythropoietin Stimulates Tumor Growth via EphB4
Abstract
While recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEpo) has been widely used to treat anemia in cancer patients, concerns about its adverse effects on patient survival have emerged. A lack of correlation between expression of the canonical EpoR and rhEpo's effects on cancer cells prompted us to consider the existence of an alternative Epo receptor. Here, we identified EphB4 as an Epo receptor that triggers downstream signaling via STAT3 and promotes rhEpo-induced tumor growth and progression. In human ovarian and breast cancer samples, expression of EphB4 rather than the canonical EpoR correlated with decreased disease-specific survival in rhEpo-treated patients. These results identify EphB4 as a critical mediator of erythropoietin-induced tumor progression and further provide clinically significant dimension to the biology of erythropoietin.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

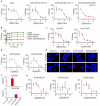
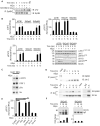
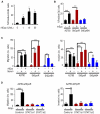
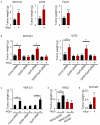

References
-
- Ahmed AA, Lu Z, Jennings NB, Etemadmoghadam D, Capalbo L, Jacamo RO, Barbosa-Morais N, Le XF, Vivas-Mejia P, Lopez-Berestein G, et al. SIK2 is a centrosome kinase required for bipolar mitotic spindle formation that provides a potential target for therapy in ovarian cancer. Cancer cell. 2010;18:109–121. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belda-Iniesta C, Perona R, Carpeno Jde C, Cejas P, Casado E, Manguan-Garcia C, Ibanez de Caceres I, Sanchez-Perez I, Andreu FB, Ferreira JA, et al. Human recombinant erythropoietin does not promote cancer growth in presence of functional receptors expressed in cancer cells. Cancer biology & therapy. 2007;6:1600–1605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 CA 096300/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA101642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 TR000943/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- CA 177909/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA177909/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 TR000943/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA109298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA098258/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA151668/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA151668/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA096300/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 16672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA083639/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA128797/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 109298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD050128/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

