Alkaline phosphatase predicts response in polycystic liver disease during somatostatin analogue therapy: a pooled analysis
- PMID: 26481454
- PMCID: PMC5497692
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.12986
Alkaline phosphatase predicts response in polycystic liver disease during somatostatin analogue therapy: a pooled analysis
Abstract
Background & aims: Somatostatin analogues reduce liver volumes in polycystic liver disease. However, patients show considerable variability in treatment responses. Our aim was to identify specific patient, disease or treatment characteristics that predict response in polycystic liver disease during somatostatin analogue therapy.
Methods: We pooled the individual patient data of four trials that evaluated long-acting somatostatin analogues (120 mg lanreotide or 40 mg octreotide) for 6-12 months in polycystic liver disease patients. We performed uni- and multivariate linear regression analysis with preselected patient, disease and drug variables to identify independent predictors of response, defined as per cent change in liver or kidney volume (in ADPKD subgroup). All analyses were adjusted for baseline liver volume and centre.
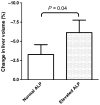
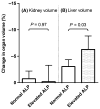
Results: We included 153 polycystic liver disease patients (86% female, median liver volume 4974 ml) from three international centres, all treated with octreotide (n = 70) or lanreotide (n = 83). Mean reduction in liver volume was 4.4% (range -31.6 to +9.4%). Multivariate linear regression revealed that elevated baseline alkaline phosphatase was associated with increased liver volume reduction during therapy (-2.7%, 95% CI -5.1 to -0.2%, P = 0.04), independently of baseline liver volume. Somatostatin analogue type, underlying diagnosis and eGFR did not affect response. In our ADPKD subpopulation (n = 100), elevated alkaline phosphatase predicted liver volume reduction (-3.2%, P = 0.03) but did not predict kidney volume reduction (+0.1%, P = 0.97). Total gastro-intestinal symptom severity decreased with therapy in a subgroup analysis (n = 95; P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Alkaline phosphatase is a liver-specific, independent predictor of response in polycystic liver disease during somatostatin analogue therapy.
Keywords: ADPKD; ADPLD; alkaline phosphatase; drug therapy; hepatic cyst; somatostatin.
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Young women with polycystic liver disease respond best to somatostatin analogues: a pooled analysis of individual patient data.Gastroenterology. 2013 Aug;145(2):357-65.e1-2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.04.055. Epub 2013 May 7. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23665274
-
Effect of lanreotide on polycystic liver and kidneys in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: an observational trial.Liver Int. 2015 May;35(5):1607-14. doi: 10.1111/liv.12726. Epub 2014 Dec 1. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 25369108
-
Lanreotide Reduces Liver Growth In Patients With Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Liver and Kidney Disease.Gastroenterology. 2019 Aug;157(2):481-491.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.04.018. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 31022403 Clinical Trial.
-
Somatostatin analogues for treatment of polycystic liver disease.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2011 May;27(3):294-300. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e328343433f. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21191289 Review.
-
Long-acting somatostatin analogue treatments in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and polycystic liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2020 Jan 9;10(1):e032620. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032620. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 31924636 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Drug holiday in patients with polycystic liver disease treated with somatostatin analogues.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2018 Oct 3;11:1756284818804784. doi: 10.1177/1756284818804784. eCollection 2018. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30302127 Free PMC article.
-
An energy-embodied paralleled liquid manipulation for equipment-free, quantitative multiplexed liver function monitoring.Sci Adv. 2025 Aug 8;11(32):eadx0092. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adx0092. Epub 2025 Aug 8. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40779627 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of a Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor and a Somatostatin Receptor Agonist Synergistically Reduces Hepatorenal Cystogenesis in an Animal Model of Polycystic Liver Disease.Am J Pathol. 2018 Apr;188(4):981-994. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.12.016. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Am J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29366679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gevers TJ, Drenth JP. Diagnosis and management of polycystic liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:101–8. - PubMed
-
- Torres VE, Harris PC, Pirson Y. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet. 2007;369:1287–301. - PubMed
-
- Wijnands TF, Neijenhuis MK, Kievit W, et al. Evaluating health-related quality of life in patients with polycystic liver disease and determining the impact of symptoms and liver volume. Liver Int. 2014;34:1578–83. - PubMed
-
- Gevers TJ, Drenth JP. Somatostatin analogues for treatment of polycystic liver disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2011;27:294–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

