Differential aging of cerebral white matter in middle-aged and older adults: A seven-year follow-up
- PMID: 26481675
- PMCID: PMC4691398
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.030
Differential aging of cerebral white matter in middle-aged and older adults: A seven-year follow-up
Abstract
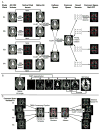
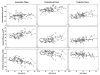
The few extant reports of longitudinal white matter (WM) changes in healthy aging, using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), reveal substantial differences in change across brain regions and DTI indices. According to the "last-in-first-out" hypothesis of brain aging late-developing WM tracts may be particularly vulnerable to advanced age. To test this hypothesis we compared age-related changes in association, commissural and projection WM fiber regions using a skeletonized, region of interest DTI approach. Using linear mixed effect models, we evaluated the influences of age and vascular risk at baseline on seven-year changes in three indices of WM integrity and organization (axial diffusivity, AD, radial diffusivity, RD, and fractional anisotropy, FA) in healthy middle-aged and older adults (mean age=65.4, SD=9.0years). Association fibers showed the most pronounced declines over time. Advanced age was associated with greater longitudinal changes in RD and FA, independent of fiber type. Furthermore, older age was associated with longitudinal RD increases in late-developing, but not early-developing projection fibers. These findings demonstrate the increased vulnerability of later developing WM regions and support the "last-in-first-out" hypothesis of brain aging.
Keywords: Age; DTI; Diffusivity; Hypertension; Longitudinal; White matter.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Bartzokis G, Sultzer D, Lu PH, Nuechterlein KH, Mintz J, Cummings JL. Heterogeneous age-related breakdown of white matter structural integrity: Implications for cortical "disconnection" in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2004;25:843–851. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.09.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D. Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson B. 1994;103:247–254. - PubMed
-
- Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S. Lme4: Linear mixed-effects models using eigen and s4. R package version 1.1–7. 2014 This is computer program (R package). The URL of the package is: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lme4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

