Surgical anatomy and pathology of the middle ear
- PMID: 26482007
- PMCID: PMC4718166
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.12389
Surgical anatomy and pathology of the middle ear
Abstract
Middle ear surgery is strongly influenced by anatomical and functional characteristics of the middle ear. The complex anatomy means a challenge for the otosurgeon who moves between preservation or improvement of highly important functions (hearing, balance, facial motion) and eradication of diseases. Of these, perforations of the tympanic membrane, chronic otitis media, tympanosclerosis and cholesteatoma are encountered most often in clinical practice. Modern techniques for reconstruction of the ossicular chain aim for best possible hearing improvement using delicate alloplastic titanium prostheses, but a number of prosthesis-unrelated factors work against this intent. Surgery is always individualized to the case and there is no one-fits-all strategy. Above all, both middle ear diseases and surgery can be associated with a number of complications; the most important ones being hearing deterioration or deafness, dizziness, facial palsy and life-threatening intracranial complications. To minimize risks, a solid knowledge of and respect for neurootologic structures is essential for an otosurgeon who must train him- or herself intensively on temporal bones before performing surgery on a patient.
Keywords: Surgical anatomy; facial nerve; middle ear; otitis media; tympanic membrane.
© 2015 Anatomical Society.
Figures
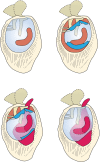
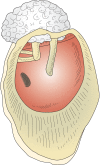
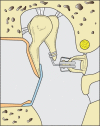
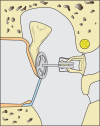
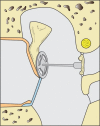
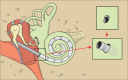
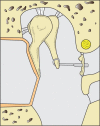
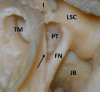
References
-
- Aggarwal R, Saeed SR, Green KJM (2006) Myringoplasty. J Laryngol Otol 120, 429–432. - PubMed
-
- Anson BDJ (1992) Surgical Anatomy of the Temporal Bone. New York: Raven Press.
-
- Atmaca S, Elmali M, Kucuk H (2014) High and dehiscent jugular bulb: clear and present danger during middle ear surgery. Surg Radiol Anat 36, 369–374. - PubMed
-
- Austin DF (1988) Reconstructive techniques for tympanosclerosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 97, 670–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

