Lignocellulose-converting enzyme activity profiles correlate with molecular systematics and phylogeny grouping in the incoherent genus Phlebia (Polyporales, Basidiomycota)
- PMID: 26482661
- PMCID: PMC4610053
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-015-0538-x
Lignocellulose-converting enzyme activity profiles correlate with molecular systematics and phylogeny grouping in the incoherent genus Phlebia (Polyporales, Basidiomycota)
Abstract
Background: The fungal genus Phlebia consists of a number of species that are significant in wood decay. Biotechnological potential of a few species for enzyme production and degradation of lignin and pollutants has been previously studied, when most of the species of this genus are unknown. Therefore, we carried out a wider study on biochemistry and systematics of Phlebia species.
Methods: Isolates belonging to the genus Phlebia were subjected to four-gene sequence analysis in order to clarify their phylogenetic placement at species level and evolutionary relationships of the genus among phlebioid Polyporales. rRNA-encoding (5.8S, partial LSU) and two protein-encoding gene (gapdh, rpb2) sequences were adopted for the evolutionary analysis, and ITS sequences (ITS1+5.8S+ITS2) were aligned for in-depth species-level phylogeny. The 49 fungal isolates were cultivated on semi-solid milled spruce wood medium for 21 days in order to follow their production of extracellular lignocellulose-converting oxidoreductases and carbohydrate active enzymes.
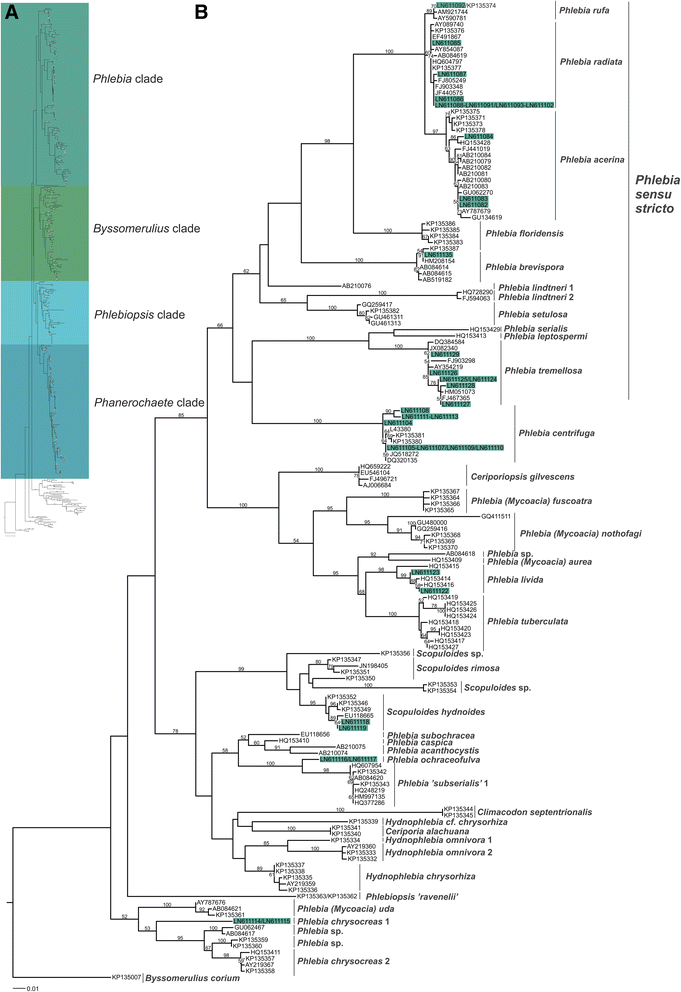
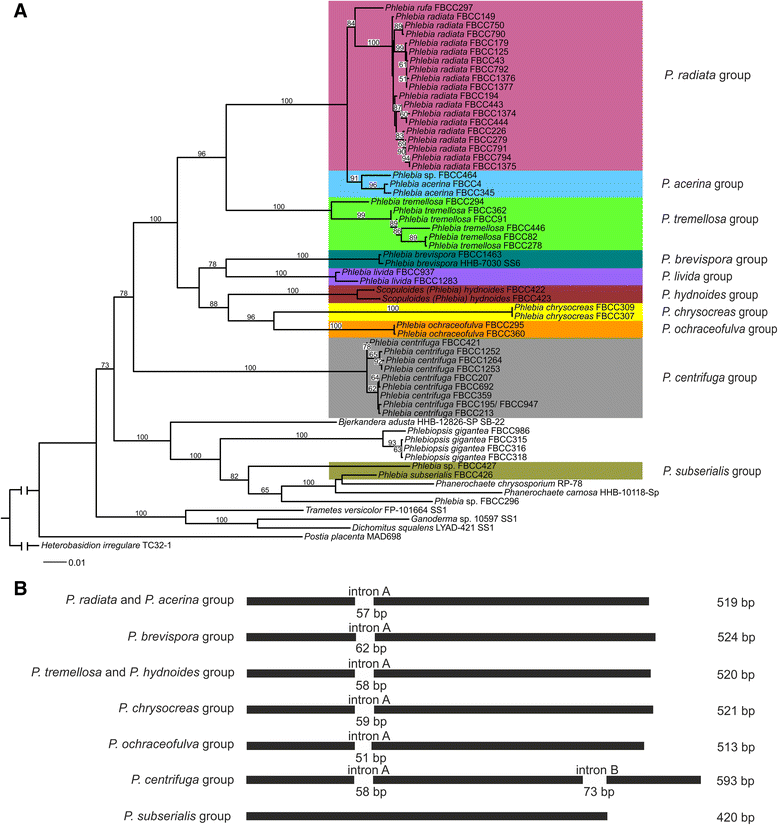
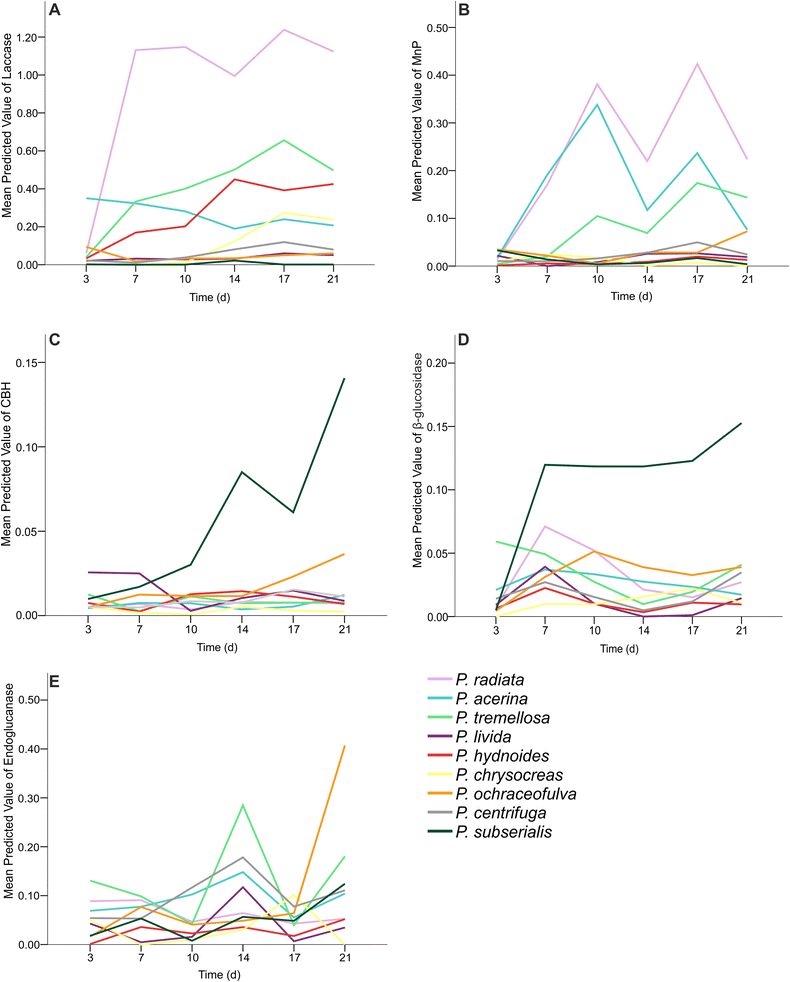
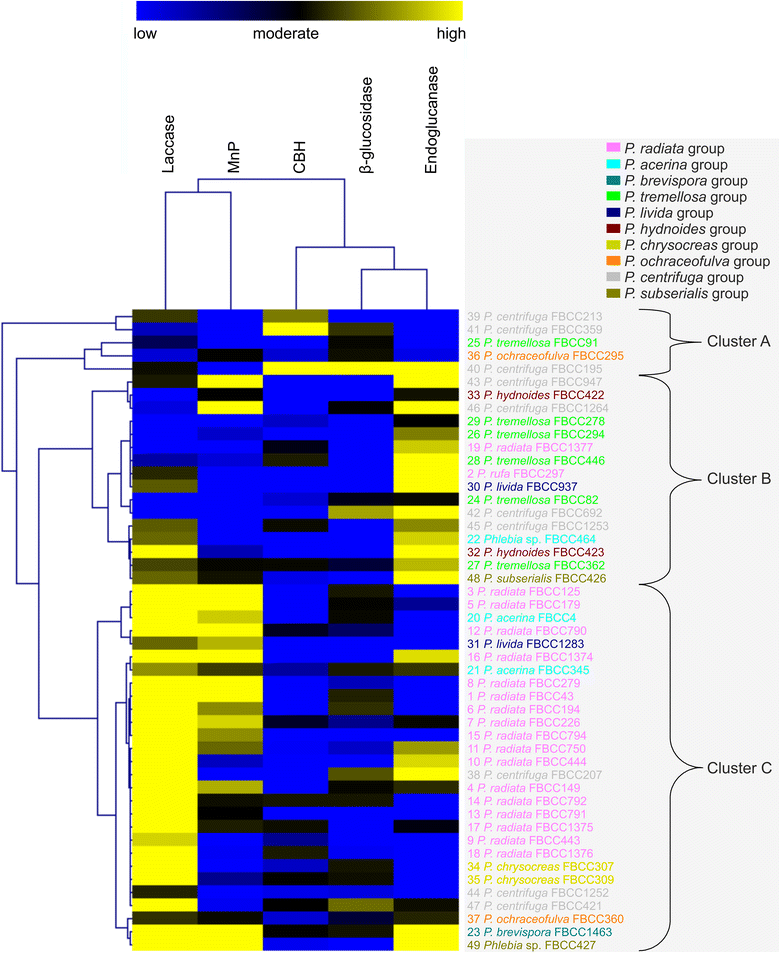
Results: Four-gene phylogenetic analysis confirmed the polyphyletic nature of the genus Phlebia. Ten species-level subgroups were formed, and their lignocellulose-converting enzyme activity profiles coincided with the phylogenetic grouping. The highest enzyme activities for lignin modification (manganese peroxidase activity) were obtained for Phlebia radiata group, which supports our previous studies on the enzymology and gene expression of this species on lignocellulosic substrates.
Conclusions: Our study implies that there is a species-level connection of molecular systematics (genotype) to the efficiency in production of both lignocellulose-converting carbohydrate active enzymes and oxidoreductases (enzyme phenotype) on spruce wood. Thus, we may propose a similar phylogrouping approach for prediction of lignocellulose-converting enzyme phenotypes in new fungal species or genetically and biochemically less-studied isolates of the wood-decay Polyporales.
Figures

References
-
- Lundell TK, Mäkelä MR, de Vries RP, Hildén KS. Genomics, lifestyles and future prospects of wood-decay and litter-decomposing basidiomycota. In: Francis MM, editor. Advances in Botanical Research, Vol 70, Fungi. London: Academic; 2014. pp. 329–370.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

