A peptide mimic blocks the cross-reaction of anti-DNA antibodies with glomerular antigens
- PMID: 26482679
- PMCID: PMC4750606
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12734
A peptide mimic blocks the cross-reaction of anti-DNA antibodies with glomerular antigens
Abstract
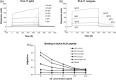
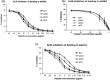
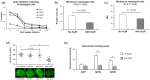
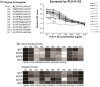
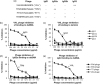
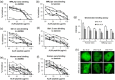
Anti-DNA antibodies play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis by cross-reacting with renal antigens. Previously, we demonstrated that the binding affinity of anti-DNA antibodies to self-antigens is isotype-dependent. Furthermore, significant variability in renal pathogenicity was seen among a panel of anti-DNA isotypes [derived from a single murine immunoglobulin (Ig)G3 monoclonal antibody, PL9-11] that share identical variable regions. In this study, we sought to select peptide mimics that effectively inhibit the binding of all murine and human anti-DNA IgG isotypes to glomerular antigens. The PL9-11 panel of IgG anti-DNA antibodies (IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b and IgG3) was used for screening a 12-mer phage display library. Binding affinity was determined by surface plasmon resonance. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), flow cytometry and glomerular binding assays were used for the assessment of peptide inhibition of antibody binding to nuclear and kidney antigens. We identified a 12 amino acid peptide (ALWPPNLHAWVP, or 'ALW') which binds to all PL9-11 IgG isotypes. Preincubation with the ALW peptide reduced the binding of the PL9-11 anti-DNA antibodies to DNA, laminin, mesangial cells and isolated glomeruli significantly. Furthermore, we confirmed the specificity of the amino acid sequence in the binding of ALW to anti-DNA antibodies by alanine scanning. Finally, ALW inhibited the binding of murine and human lupus sera to dsDNA and glomeruli significantly. In conclusion, by inhibiting the binding of polyclonal anti-DNA antibodies to autoantigens in vivo, the ALW peptide (or its derivatives) may potentially be a useful approach to block anti-DNA antibody binding to renal tissue.
Keywords: SLE; anti-DNA antibodies; lupus nephritis; phage display library.
© 2015 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The constant region contributes to the antigenic specificity and renal pathogenicity of murine anti-DNA antibodies.J Autoimmun. 2012 Dec;39(4):398-411. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2012.06.005. Epub 2012 Jul 28. J Autoimmun. 2012. PMID: 22841793 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-DNA antibody mediated catalysis is isotype dependent.Mol Immunol. 2016 Jan;69:33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Mol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26655427 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-reactivity of human lupus anti-DNA antibodies with alpha-actinin and nephritogenic potential.Arthritis Rheum. 2005 Feb;52(2):522-30. doi: 10.1002/art.20862. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. PMID: 15693007
-
Antigenic triggers and molecular targets for anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies.Lupus. 2002;11(12):865-71. doi: 10.1191/0961203302lu308rr. Lupus. 2002. PMID: 12529052 Review.
-
A peptide DNA surrogate that binds and inhibits anti-dsDNA antibodies.Clin Immunol. 2005 Dec;117(3):214-20. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2005.09.013. Epub 2005 Nov 11. Clin Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16290070 Review.
Cited by
-
Fn14 Deficiency Ameliorates Anti-dsDNA IgG-Induced Glomerular Damage in SCID Mice.J Immunol Res. 2018 Dec 16;2018:1256379. doi: 10.1155/2018/1256379. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30648117 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Double-Stranded DNA IgG Participates in Renal Fibrosis through Suppressing the Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 Signals.Front Immunol. 2017 May 31;8:610. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00610. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28620377 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in precision medicine for lupus nephritis: biomarker- and AI-driven diagnosis and treatment response prediction and targeted therapies.EBioMedicine. 2025 Jul;117:105785. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105785. Epub 2025 Jun 3. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40466435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defective Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 Signaling Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2017 Oct 16;8:1292. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01292. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29085365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-double Stranded DNA Antibodies: Origin, Pathogenicity, and Targeted Therapies.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 17;10:1667. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01667. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31379858 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yung S, Chan TM. Anti‐DNA antibodies in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis – the emerging mechanisms. Autoimmun Rev 2008; 7:317–21. - PubMed
-
- Putterman C. New approaches to the renal pathogenicity of anti‐DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 2004; 3:7–11. - PubMed
-
- Qing X, Zavadil J, Crosby MB et al Nephritogenic anti‐DNA antibodies regulate gene expression in MRL/lpr mouse glomerular mesangial cells. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54:2198–210. - PubMed
-
- Yung S, Tsang RC, Sun Y, Leung JK, Chan TM. Effect of human anti‐DNA antibodies on proximal renal tubular epithelial cell cytokine expression: implications on tubulointerstitial inflammation in lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005; 16:3281–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

