Highly Branched Xylan Made by IRREGULAR XYLEM14 and MUCILAGE-RELATED21 Links Mucilage to Arabidopsis Seeds
- PMID: 26482889
- PMCID: PMC4677919
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.15.01441
Highly Branched Xylan Made by IRREGULAR XYLEM14 and MUCILAGE-RELATED21 Links Mucilage to Arabidopsis Seeds
Abstract
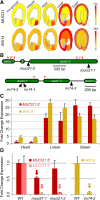
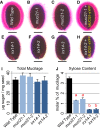
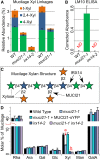
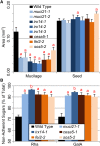
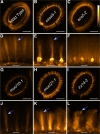
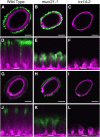
All cells of terrestrial plants are fortified by walls composed of crystalline cellulose microfibrils and a variety of matrix polymers. Xylans are the second most abundant type of polysaccharides on Earth. Previous studies of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) irregular xylem (irx) mutants, with collapsed xylem vessels and dwarfed stature, highlighted the importance of this cell wall component and revealed multiple players required for its synthesis. Nevertheless, xylan elongation and substitution are complex processes that remain poorly understood. Recently, seed coat epidermal cells were shown to provide an excellent system for deciphering hemicellulose production. Using a coexpression and sequence-based strategy, we predicted several MUCILAGE-RELATED (MUCI) genes that encode glycosyltransferases (GTs) involved in the production of xylan. We now show that MUCI21, a member of an uncharacterized clade of the GT61 family, and IRX14 (GT43 protein) are essential for the synthesis of highly branched xylan in seed coat epidermal cells. Our results reveal that xylan is the most abundant xylose-rich component in Arabidopsis seed mucilage and is required to maintain its architecture. Characterization of muci21 and irx14 single and double mutants indicates that MUCI21 is a Golgi-localized protein that likely facilitates the addition of xylose residues directly to the xylan backbone. These unique branches seem to be necessary for pectin attachment to the seed surface, while the xylan backbone maintains cellulose distribution. Evaluation of muci21 and irx14 alongside mutants that disrupt other wall components suggests that mucilage adherence is maintained by complex interactions between several polymers: cellulose, xylans, pectins, and glycoproteins.
© 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Xylan synthesized by Irregular Xylem 14 (IRX14) maintains the structure of seed coat mucilage in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2016 Mar;67(5):1243-57. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv510. Epub 2016 Feb 1. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 26834178 Free PMC article.
-
KNAT7 regulates xylan biosynthesis in Arabidopsis seed-coat mucilage.J Exp Bot. 2020 Jul 6;71(14):4125-4139. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa189. J Exp Bot. 2020. PMID: 32277756
-
Xylans Provide the Structural Driving Force for Mucilage Adhesion to the Arabidopsis Seed Coat.Plant Physiol. 2016 May;171(1):165-78. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00211. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26979331 Free PMC article.
-
A review of xylan and lignin biosynthesis: foundation for studying Arabidopsis irregular xylem mutants with pleiotropic phenotypes.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 May-Jun;49(3):212-41. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2014.889651. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24564339 Review.
-
Sticking to cellulose: exploiting Arabidopsis seed coat mucilage to understand cellulose biosynthesis and cell wall polysaccharide interactions.New Phytol. 2017 May;214(3):959-966. doi: 10.1111/nph.14468. Epub 2017 Feb 13. New Phytol. 2017. PMID: 28191645 Review.
Cited by
-
Transport of UDP-rhamnose by URGT2, URGT4, and URGT6 modulates rhamnogalacturonan-I length.Plant Physiol. 2021 Apr 2;185(3):914-933. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiaa070. Plant Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33793913 Free PMC article.
-
Mucilage extracted from Chilean papaya seeds is enriched with homogalacturonan domains.Front Plant Sci. 2024 May 30;15:1380533. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1380533. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38872878 Free PMC article.
-
The Modification of Plant Cell Wall Polysaccharides in Potato Plants during Pectobacterium atrosepticum-Caused Infection.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jul 9;10(7):1407. doi: 10.3390/plants10071407. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34371610 Free PMC article.
-
Convergent Emergence of Glucomannan β-Galactosyltransferase Activity in Asterids and Rosids.Plant Cell Physiol. 2024 Dec 21;65(12):2030-2039. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcae118. Plant Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39392710 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosyltransferase Family 61 in Liliopsida (Monocot): The Story of a Gene Family Expansion.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Dec 11;9:1843. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01843. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30619412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

