Population pharmacokinetics of nalmefene in healthy subjects and its relation to μ-opioid receptor occupancy
- PMID: 26483076
- PMCID: PMC4833148
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12805
Population pharmacokinetics of nalmefene in healthy subjects and its relation to μ-opioid receptor occupancy
Abstract
Aims: The aims of this study were to develop a population pharmacokinetic (PK) model to describe the PK of nalmefene in healthy subjects and to relate the exposure of nalmefene to the μ-opioid receptor occupancy by simulations in the target population.
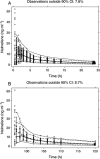
Methods: Data from nine phase I studies (243 subjects) with extensive blood sampling were pooled and used for the population PK model building. Data from four other phase I studies (85 subjects) were pooled and used as an external validation dataset. Eight subjects from an imaging study contributed occupancy data and the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) relationship was modelled. Combining the population PK model and the PK/PD relationship enabled simulations to predict μ-opioid occupancy.
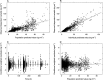
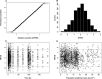
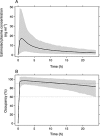
Results: A two compartment model with first order absorption best described the nalmefene PK data. The typical subject in the population was estimated to have a systemic clearance of 60.4 l h(-1) and a central volume of distribution of 266 l. Absolute oral bioavailability was estimated to 41% without food intake and with food about 53%. Simulation of the μ-opioid receptor occupancy shows that the 95% confidence bound is within or above 60-90% occupancy for up to 22-24 h after a single dose of 20 mg nalmefene.
Conclusions: A robust population PK model for nalmefene was developed. Based on the concentration-occupancy model the μ-opioid receptor occupancy after a single 20 mg dose of nalmefene is predicted to be above the target therapeutic occupancy for about 24 h in about 95% of the target population.
Keywords: alcohol dependence; healthy subjects; nalmefene; opioid antagonist; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics.
© 2015 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prolonged central mu-opioid receptor occupancy after single and repeated nalmefene dosing.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005 Dec;30(12):2245-53. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300790. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005. PMID: 15956985 Clinical Trial.
-
[Pharmacokinetics of nalmefene after a single or multiple intravenous doses in Chinese healthy volunteers].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2008 Oct;28(10):1816-9. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18971181 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Nalmefene induced elevation in serum prolactin in normal human volunteers: partial kappa opioid agonist activity?Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005 Dec;30(12):2254-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300811. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005. PMID: 15988468
-
[Pharmacological profile and clinical findings of nalmefene (Selincro®) for reducing alcohol consumption in patients with alcohol dependence].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2020;155(2):113-119. doi: 10.1254/fpj.19136. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2020. PMID: 32115477 Review. Japanese.
-
Nalmefene for the treatment of alcohol use disorders: recent data and clinical potential.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016;17(4):619-26. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2016.1146689. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 26810044 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of nalmefene on the impulsive and reflective system in alcohol use disorder: A resting-state fMRI study.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Aug;239(8):2471-2489. doi: 10.1007/s00213-022-06137-1. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35426492 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetic Properties of an FDA-approved Intranasal Nalmefene Formulation for the Treatment of Opioid Overdose.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2024 Jan;13(1):58-69. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.1312. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2024. PMID: 37496452 Free PMC article.
-
Nalmefene Hydrochloride: Potential Implications for Treating Alcohol and Opioid Use Disorder.Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2024 Apr 3;15:43-57. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S431270. eCollection 2024. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38585160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nalmefene vs. dexmedetomidine for prevention of postoperative hyperalgesia in patients undergoing laparoscopic gynecological surgery with remifentanil infusion: A randomized double-blind controlled trial.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 25;14:1131812. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1131812. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36762101 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroendocrine effects of naltrexone versus nalmefene in humans.Hum Psychopharmacol. 2020 Mar;35(2):e2726. doi: 10.1002/hup.2726. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32050055 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bart G, Schluger JH, Borg L, Ho A, Bidlack JM, Kreek MJ. Nalmefene induced elevation in serum prolactin in normal human volunteers: partial kappa opioid agonist activity? Neuropsychopharmacology 2005; 30: 2254–62. - PubMed
-
- Guerrero M, Urbano M, Brown SJ, Cayanan C, Ferguson J, Cameron M, Devi LA, Roberts E, Rosen H. Optimization and characterization of an opioid kappa receptor (OPRK1) antagonist. Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010. 2013 Apr 15 [updated 2013 Nov 14]. - PubMed
-
- EMA . Selincro: EPAR prodution information. Annex I – summary of product characteristics. Available at www.ema.europa.eu [homepage on internet] (last accessed 2 October 2015).
-
- Gual A, He Y, Torup L, van den Brick W, Mann K. A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, efficacy study of nalmefene, as‐needed use, in patients with alcohol dependence. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2013; 23: 1432–42. - PubMed
-
- Mann K, Bladström A, Torup L, Gual A, van den Brink W. Extending the treatment options in alcohol dependence: a randomized controlled study of as‐needed nalmefene. Biol Psychiatry 2013; 73: 706–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

