Carcinoma cells induce lumen filling and EMT in epithelial cells through soluble E-cadherin-mediated activation of EGFR
- PMID: 26483386
- PMCID: PMC4712814
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.173518
Carcinoma cells induce lumen filling and EMT in epithelial cells through soluble E-cadherin-mediated activation of EGFR
Abstract
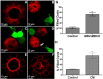
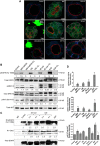
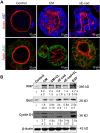
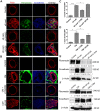
In epithelial cancers, carcinoma cells coexist with normal cells. Although it is known that the tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a pivotal role in cancer progression, it is not completely understood how the tumor influences adjacent normal epithelial cells. In this study, a three-dimensional co-culture system comprising non-transformed epithelial cells (MDCK) and transformed carcinoma cells (MSV-MDCK) was used to demonstrate that carcinoma cells sequentially induce preneoplastic lumen filling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in epithelial cysts. MMP-9 secreted by carcinoma cells cleaves cellular E-cadherin (encoded by CDH1) from epithelial cells to generate soluble E-cadherin (sE-cad), a pro-oncogenic protein. We show that sE-cad induces EGFR activation, resulting in lumen filling in MDCK cysts. Long-term sE-cad treatment induced EMT. sE-cad caused lumen filling by induction of the ERK signaling pathway and triggered EMT through the sustained activation of the AKT pathway. Although it is known that sE-cad induces MMP-9 release and consequent EGFR activation in tumor cells, our results, for the first time, demonstrate that carcinoma cells can induce sE-cad shedding in adjacent epithelial cells, which leads to EGFR activation and the eventual transdifferentiation of the normal epithelial cells.
Keywords: EGFR; MMP-9; Soluble E-cadherin; Transdifferentiation.
© 2015. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activation of EGFR promotes squamous carcinoma SCC10A cell migration and invasion via inducing EMT-like phenotype change and MMP-9-mediated degradation of E-cadherin.J Cell Biochem. 2011 Sep;112(9):2508-17. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23175. J Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21557297
-
DN-R175H p53 mutation is more effective than p53 interference in inducing epithelial disorganization and activation of proliferation signals in human carcinoma cells: role of E-cadherin.Int J Cancer. 2009 Oct 1;125(7):1604-12. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24512. Int J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19507255
-
Phospho-Akt pathway activation and inhibition depends on N-cadherin or phospho-EGFR expression in invasive human bladder cancer cell lines.Urol Oncol. 2010 Mar-Apr;28(2):180-8. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2008.09.041. Epub 2008 Dec 12. Urol Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19070520
-
Soluble E-cadherin: more than a symptom of disease.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jan 1;17(5):1948-64. doi: 10.2741/4031. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22201848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview on the Role of E-Cadherin in Gastric Cancer: Dysregulation and Clinical Implications.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jul 30;8:689139. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.689139. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34422902 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer cells corrupt normal epithelial cells through miR-let-7c-rich small extracellular vesicle-mediated downregulation of p53/PTEN.Int J Oral Sci. 2022 Jul 19;14(1):36. doi: 10.1038/s41368-022-00192-2. Int J Oral Sci. 2022. PMID: 35851058 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of fibroblasts to tunnel formation and inflammation in hidradenitis suppurativa/ acne inversa.Exp Dermatol. 2019 Aug;28(8):886-891. doi: 10.1111/exd.13978. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Exp Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 31140657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SNU-333 Cells as an Appropriate Cell Line for the Orthotopic Renal Cell Carcinoma Model.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:15330338211038487. doi: 10.1177/15330338211038487. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34490820 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Adhesion Molecules as Modulators of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor.Cells. 2024 Nov 19;13(22):1919. doi: 10.3390/cells13221919. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39594667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S100A4 Is Involved in Stimulatory Effects Elicited by the FGF2/FGFR1 Signaling Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 29;22(9):4720. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094720. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33946884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brouxhon S., Kyrkanides S., O'Banion M. K., Johnson R., Pearce D. A., Centola G. M., Miller J.-n. N., McGrath K. H., Erdle B., Scott G. et al. (2007). Sequential down-regulation of E-cadherin with squamous cell carcinoma progression: loss of E-cadherin via a prostaglandin E2-EP2 dependent posttranslational mechanism. Cancer Res. 67, 7654-7664. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4415 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

