Survival of human lymphoma cells requires B-cell receptor engagement by self-antigens
- PMID: 26483459
- PMCID: PMC4640740
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1514944112
Survival of human lymphoma cells requires B-cell receptor engagement by self-antigens
Abstract
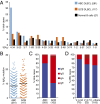
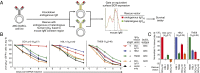
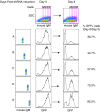
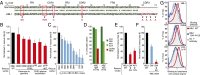
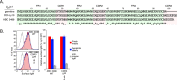
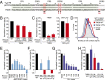
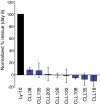
The activated B-cell-like (ABC) subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) relies on chronic active B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling. BCR pathway inhibitors induce remissions in a subset of ABC DLBCL patients. BCR microclusters on the surface of ABC cells resemble those generated following antigen engagement of normal B cells. We speculated that binding of lymphoma BCRs to self-antigens initiates and maintains chronic active BCR signaling in ABC DLBCL. To assess whether antigenic engagement of the BCR is required for the ongoing survival of ABC cells, we developed isogenic ABC cells that differed solely with respect to the IgH V region of their BCRs. In competitive assays with wild-type cells, substitution of a heterologous V region impaired the survival of three ABC lines. The viability of one VH4-34(+) ABC line and the ability of its BCR to bind to its own cell surface depended on V region residues that mediate the intrinsic autoreactivity of VH4-34 to self-glycoproteins. The BCR of another ABC line reacted with self-antigens in apoptotic debris, and the survival of a third ABC line was sustained by reactivity of its BCR to an idiotypic epitope in its own V region. Hence, a diverse set of self-antigens is responsible for maintaining the malignant survival of ABC DLBCL cells. IgH V regions used by the BCRs of ABC DLBCL biopsy samples varied in their ability to sustain survival of these ABC lines, suggesting a screening procedure to identify patients who might benefit from BCR pathway inhibition.
Keywords: B-cell receptor; cancer biology; lymphoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


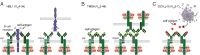
Similar articles
-
Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Nature. 2010 Jan 7;463(7277):88-92. doi: 10.1038/nature08638. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20054396 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial BTK and MALT1 inhibition augments killing of CD79 mutant diffuse large B cell lymphoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 8;6(39):42232-42. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6273. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26540570 Free PMC article.
-
MYC Protein-positive Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Features an Activated B-Cell Receptor Signal Pathway.Am J Surg Pathol. 2017 Apr;41(4):541-549. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000799. Am J Surg Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28291124
-
B-cell receptor signaling as a driver of lymphoma development and evolution.Semin Cancer Biol. 2013 Dec;23(6):410-21. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Semin Cancer Biol. 2013. PMID: 24060900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B-cell receptor signaling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Semin Hematol. 2015 Apr;52(2):77-85. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2015.01.008. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Semin Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25805587 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Aged/Autoimmune B-cell Program Defines the Early Transformation of Extranodal Lymphomas.Cancer Discov. 2023 Jan 9;13(1):216-243. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0561. Cancer Discov. 2023. PMID: 36264161 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the CARMA1/BCL10/MALT1 complex in lymphoid malignancies.Curr Opin Hematol. 2016 Jul;23(4):402-9. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000257. Curr Opin Hematol. 2016. PMID: 27135977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An EBNA3C-deleted Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) mutant causes B-cell lymphomas with delayed onset in a cord blood-humanized mouse model.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Aug 20;14(8):e1007221. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007221. eCollection 2018 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30125329 Free PMC article.
-
IgD attenuates the IgM-induced anergy response in transitional and mature B cells.Nat Commun. 2016 Nov 10;7:13381. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13381. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27830696 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-SRC kinase inhibition blocks B-cell receptor oncogenic signaling in non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Blood. 2018 May 24;131(21):2345-2356. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-10-809210. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29567799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dameshek W, Schwartz RS. Leukemia and auto-immunization—Some possible relationships. Blood. 1959;14:1151–1158. - PubMed
-
- Küppers R. Mechanisms of B-cell lymphoma pathogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(4):251–262. - PubMed
-
- Quinn ER, et al. The B-cell receptor of a hepatitis C virus (HCV)-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma binds the viral E2 envelope protein, implicating HCV in lymphomagenesis. Blood. 2001;98(13):3745–3749. - PubMed
-
- Wotherspoon AC, et al. Regression of primary low-grade B-cell gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1993;342(8871):575–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

