Trait rejection sensitivity is associated with vigilance and defensive response rather than detection of social rejection cues
- PMID: 26483750
- PMCID: PMC4591508
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01516
Trait rejection sensitivity is associated with vigilance and defensive response rather than detection of social rejection cues
Abstract
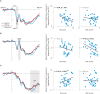
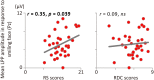
Prior studies suggest that psychological difficulties arise from higher trait Rejection Sensitivity (RS)-heightened vigilance and differential detection of social rejection cues and defensive response to. On the other hand, from an evolutionary perspective, rapid and efficient detection of social rejection cues can be considered beneficial. We conducted a survey and an electrophysiological experiment to reconcile this seeming contradiction. We compared the effects of RS and Rejection Detection Capability (RDC) on perceived interpersonal experiences (Study 1) and on neurocognitive processes in response to cues of social rejection (disgusted faces; Study 2). We found that RS and RDC were not significantly related, although RS was positively related to perceived social rejection experiences and RDC was positively related to perceived social inclusion experiences. Event-related brain potentials (ERPs) revealed that higher RS was related to cognitive avoidance (i.e., P1) and heightened motivated attention (i.e., late positive potential: LPP), but not to facial expression encoding (i.e., N170) toward disgusted faces. On the other hand, higher RDC was related to heightened N170 amplitude, but not to P1 and LPP amplitudes. These findings imply that sensitivity to rejection is apparently distinct from the ability to detect social rejection cues and instead reflects intense vigilance and defensive response to those cues. We discussed an alternative explanation of the relationship between RS and RDC from a signal detection perspective.
Keywords: N170; P1; event-related brain potentials; evolutionary perspective; late positive potential; rejection sensitivity; social inclusion; social rejection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emotional face prediction in rejection sensitive individuals: Evidence from event-related potentials.Conscious Cogn. 2020 Feb;78:102880. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2020.102880. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Conscious Cogn. 2020. PMID: 31954983
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy attenuates the enhanced early facial stimuli processing in social anxiety disorders: an ERP investigation.Behav Brain Funct. 2017 Jul 28;13(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12993-017-0130-7. Behav Brain Funct. 2017. PMID: 28754179 Free PMC article.
-
Social exclusion induces early-stage perceptual and behavioral changes in response to social cues.Soc Neurosci. 2014;9(2):174-85. doi: 10.1080/17470919.2014.883325. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Soc Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24499456
-
Greater positive schizotypy relates to reduced N100 activity during rejection scenes.Neuropsychologia. 2014 Aug;61:280-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.06.031. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Neuropsychologia. 2014. PMID: 25010933
-
The link between rejection sensitivity and borderline personality disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Clin Psychol. 2019 Sep;58(3):289-326. doi: 10.1111/bjc.12216. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Br J Clin Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30900278
Cited by
-
Exploring Intergroup Peer Exclusion: Validation of the Latency Social-Psychological Developmental Questionnaire (LSPD).Children (Basel). 2023 Mar 13;10(3):543. doi: 10.3390/children10030543. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980101 Free PMC article.
-
An Examination of the Relationship between Discrimination, Depression, and Hypertension in Native Hawaiians.Asian Am J Psychol. 2019;10(3):249-257. doi: 10.1037/aap0000151. Asian Am J Psychol. 2019. PMID: 33224437 Free PMC article.
-
Quality-checking a novel "fact sheet" on ghostly episodes.Front Psychol. 2025 Jul 1;16:1585437. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1585437. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40667394 Free PMC article.
-
Heightened neural sensitivity to social exclusion in boys with a history of low peer preference during primary school.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2019 Aug;38:100673. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2019.100673. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31252200 Free PMC article.
-
Heightened neural sensitivity to social exclusion in boys with a history of low peer preference during primary school.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2020 Aug;44:100792. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2020.100792. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32716848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoki S., Suzuki S., Yanai H. (1974). A new trial of making a health and personality inventry, THPI. Jpn. J. Behaviometrics 2 41–53.
-
- Ayduk O., Downey G., Kim M. (2001). Rejection sensitivity and depressive symptoms in women. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 27 868–878. 10.1177/0146167201277009 - DOI
-
- Ayduk O., Downey G., Testa A., Yen Y., Shoda Y. (1999). Does rejection elicit hostility in rejection sensitive women? Soc. Cogn. 17 245–271. 10.1521/soco.1999.17.2.245 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

