Interplay between Transcription Factors and the Epigenome: Insight from the Role of RUNX1 in Leukemia
- PMID: 26483790
- PMCID: PMC4586508
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00499
Interplay between Transcription Factors and the Epigenome: Insight from the Role of RUNX1 in Leukemia
Abstract
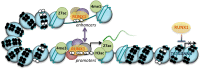
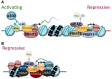
The genome has the ability to respond in a precise and co-ordinated manner to cellular signals. It achieves this through the concerted actions of transcription factors and the chromatin platform, which are targets of the signaling pathways. Our understanding of the molecular mechanisms through which transcription factors and the chromatin landscape each control gene activity has expanded dramatically over recent years, and attention has now turned to understanding the complex, multifaceted interplay between these regulatory layers in normal and disease states. It has become apparent that transcription factors as well as the components and modifiers of the epigenetic machinery are frequent targets of genomic alterations in cancer cells. Through the study of these factors, we can gain unique insight into the dynamic interplay between transcription factors and the epigenome, and how their dysregulation leads to aberrant gene expression programs in cancer. Here, we will highlight how these factors normally co-operate to establish and maintain the transcriptional and epigenetic landscape of cells, and how this is reprogramed in cancer, focusing on the RUNX1 transcription factor and oncogenic derivative RUNX1-ETO in leukemia as paradigms of transcriptional and epigenetic reprograming.
Keywords: RUNX1; cancer; chromatin; epigenetic mechanisms; epigenome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of the GM-CSF promoter by RUNX1.Leuk Res. 2010 Sep;34(9):1203-13. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2010.03.029. Epub 2010 May 1. Leuk Res. 2010. PMID: 20439113
-
Epigenetic regulation of inducible gene expression in the immune system.Immunology. 2013 Jul;139(3):285-93. doi: 10.1111/imm.12100. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23521628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond transcription factors: how oncogenic signalling reshapes the epigenetic landscape.Nat Rev Cancer. 2016 Jun;16(6):359-72. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.41. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27220480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Epigenetic Regulation in Transcriptional Memory in the Immune System.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017;106:43-69. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017. PMID: 28057215 Review.
-
Core binding factor genes and human leukemia.Haematologica. 2002 Dec;87(12):1307-23. Haematologica. 2002. PMID: 12495904 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of MYB by distal enhancer elements in human myeloid leukemia.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Feb 26;12(2):223. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03515-z. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33637692 Free PMC article.
-
RUNX represses Pmp22 to drive neurofibromagenesis.Sci Adv. 2019 Apr 24;5(4):eaau8389. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau8389. eCollection 2019 Apr. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31032403 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription of the Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 2B (HTR2B) Gene Is under the Regulatory Influence of the Transcription Factors NFI and RUNX1 in Human Uveal Melanoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 21;19(10):3272. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103272. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30347896 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Mimics Exercise-Induced Changes in Skeletal Muscle Gene Expression in Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jun 1;105(6):2027-41. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa165. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32232327 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin dysregulation associated with NSD1 mutation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Rep. 2021 Feb 23;34(8):108769. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108769. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 33626351 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

