Temporal sleep patterns in adults using actigraph
- PMID: 26483920
- PMCID: PMC4559592
- DOI: 10.1016/j.slsci.2014.09.012
Temporal sleep patterns in adults using actigraph
Abstract
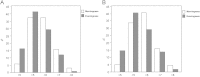
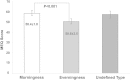
The aim of the present study was to characterize the temporal patterns of sleep and wakefulness in a sample of the adult subjects from São Paulo city. All subjects filled the Morningness/Eveningness Questionnaire (MEQ) and wore an actigraph for at least three consecutive days. A total of 359 subjects were considered for the analyses. The mean age was 43±14 years, the mean body mass index was 26.7±5.7 kg/m(2), and 60% were female. The mean MEQ score was 58.0±10.7. The sleep pattern evaluated by the actigraphic analyses showed that 92% had a monophasic sleep pattern, 7% biphasic, and 1% polyphasic sleep pattern. Cluster analysis, based on time to sleep onset, sleep efficiency, sleep latency, and total sleep time, was able to identify three different groups denominated: morning type, evening type, and undefined type. Morning type subjects were more frequent, older, and had higher MEQ scores than evening type subjects. Our results showed that the actigraph objectively assessed the sleep-wake cycle and was able to discriminate between morning and evening type individuals. These findings suggest that the actigraph could be a valuable tool for assessing temporal sleep patterns, including the circadian preferences.
Keywords: Actigraph; Circadian preferences; Eveningness; Morningness; Sleep-wake pattern; Temporal patterns.
Figures


References
-
- Lauderdale DS, Knutson KL, Yan LL, Rathouz PJ, Hulley SB, Sidney S. Objectively measured sleep characteristics among early-middle-aged adults: the CARDIA study. Am J Epidemiol. 2006;164(1):5–16. - PubMed
-
- Jean-Louis G, Kripke DF, Ancoli-Israel S, Klauber MR, Sepulveda RS. Sleep duration, illumination, and activity patterns in a population sample: effects of gender and ethnicity. Biol Psychiat. 2000;47:921–927. - PubMed
-
- Paine SJ, Gander PH, Travier N. The epidemiology of morningness/eveningness: influence of age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic factors in adults (30-49 years) J Biol Rhythm. 2006;21(1):68–76. - PubMed
-
- Chelminski I, Ferraro FR, Petros T, Plaud JJ. Horne and Ostberg questionnaire: a score distribution in a large sample of young adults. Pers Indiv Differ. 1997;23:647–652.
-
- Adan A, Natale V. Gender differences in morningness-eveningness preference. Chronobiol Int. 2002;19(4):709–720. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

