Comparison of genomic DNA methylation pattern among septic and non-septic newborns - An epigenome wide association study
- PMID: 26484145
- PMCID: PMC4535661
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gdata.2014.11.004
Comparison of genomic DNA methylation pattern among septic and non-septic newborns - An epigenome wide association study
Abstract
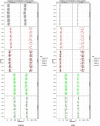
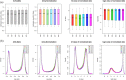
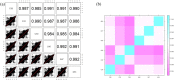
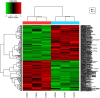
DNA methylation is the current strategy in the field of biomarker discovery due to its prognostic efficiency. Its role in prognosis and early diagnosis has been recognized in various types of cancer. Sepsis still remains one of the major causes of neonatal mortality. Delay in diagnosis of sepsis leads to treatment difficulties and poor outcome. In this study, we have done an epigenome wide search to identify potential markers for prognosis of neonatal sepsis which may improve the treatment strategies. We analyzed the CpG methylation status in the epigenome of three septic and non-septic babies using Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450K methylation microarray. The microarray data was analyzed with Illumina GenomeStudio v2011.1. After screening for biological and clinical significance, we found 81 differentially methylated CpGs located in 64 genes. Bioinformatic analysis using DAVID and GeneMania revealed a panel of differentially methylated protocadherin beta (PCDHB) genes that play vital role in leukocyte cell adhesion and Wnt signaling pathway. Apart, genes like CCS, DNAJA3, and DEGS2 were potentially hyper/hypo methylated which can be utilized in the development of novel biomarkers. This study will be helpful in exploring the role of DNA methylation in the pathophysiology of neonatal sepsis. The complete microarray data can be accessed from the public domain, Gene Expression Omnibus of NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). The accession number is GSE58651.
Keywords: CpG sites; DNA methylation; Epigenetics; Microarray; Neonatal sepsis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genome-wide DNA methylation differences according to oestrogen receptor beta status in colorectal cancer.Epigenetics. 2019 May;14(5):477-493. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2019.1595998. Epub 2019 Mar 30. Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 30931802 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenome-wide discovery and evaluation of leukocyte DNA methylation markers for the detection of colorectal cancer in a screening setting.Clin Epigenetics. 2017 Mar 3;9:24. doi: 10.1186/s13148-017-0322-x. eCollection 2017. Clin Epigenetics. 2017. PMID: 28270869 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenome-wide DNA methylation profiling in septic and non-septic patients with similar infections: potential use as sepsis biomarkers.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jan 24;14:1532417. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1532417. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39926115 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenome-wide study for the offspring exposed to maternal HBV infection during pregnancy, a pilot study.Gene. 2018 Jun 5;658:76-85. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.03.025. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29526602
-
Epigenome-wide association studies in asthma: A systematic review.Clin Exp Allergy. 2019 Jul;49(7):953-968. doi: 10.1111/cea.13403. Epub 2019 May 14. Clin Exp Allergy. 2019. PMID: 31009112
Cited by
-
DNA Methylation Analysis to Unravel Altered Genetic Pathways Underlying Early Onset and Late Onset Neonatal Sepsis. A Pilot Study.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 15;12:622599. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.622599. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33659006 Free PMC article.
-
Early Diagnosis of Sepsis: Is an Integrated Omics Approach the Way Forward?Mol Diagn Ther. 2017 Oct;21(5):525-537. doi: 10.1007/s40291-017-0282-z. Mol Diagn Ther. 2017. PMID: 28624903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Host Cell DNA Methylation in the Immune Response to Bacterial Infection.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 29;12:696280. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.696280. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34394088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylation levels at individual age-associated CpG sites can be indicative for life expectancy.Aging (Albany NY). 2016 Feb;8(2):394-401. doi: 10.18632/aging.100908. Aging (Albany NY). 2016. PMID: 26928272 Free PMC article.
-
VDAC Genes Expression and Regulation in Mammals.Front Physiol. 2021 Aug 5;12:708695. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.708695. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34421651 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Villar J., Cabrera N.E., Casula M., Valladares F., Flores C., López-Aguilar J. WNT/β-catenin signaling is modulated by mechanical ventilation in an experimental model of acute lung injury. Intensive Care Med. 2011;37(7):1201–1209. - PubMed
-
- Ying J., Gao Z., Li H., Srivastava G., Murray P.G., Goh H.K. Frequent epigenetic silencing of protocadherin 10 by methylation in multiple haematologic malignancies. Br. J. Haematol. 2007;136:829–832. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

