Image-guided radiation therapy in lymphoma management
- PMID: 26484299
- PMCID: PMC4607569
- DOI: 10.3857/roj.2015.33.3.161
Image-guided radiation therapy in lymphoma management
Abstract
Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) is a process of incorporating imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Positron emission tomography (PET), and ultrasound (US) during radiation therapy (RT) to improve treatment accuracy. It allows real-time or near real-time visualization of anatomical information to ensure that the target is in its position as planned. In addition, changes in tumor volume and location due to organ motion during treatment can be also compensated. IGRT has been gaining popularity and acceptance rapidly in RT over the past 10 years, and many published data have been reported on prostate, bladder, head and neck, and gastrointestinal cancers. However, the role of IGRT in lymphoma management is not well defined as there are only very limited published data currently available. The scope of this paper is to review the current use of IGRT in the management of lymphoma. The technical and clinical aspects of IGRT, lymphoma imaging studies, the current role of IGRT in lymphoma management and future directions will be discussed.
Keywords: Adaptive radiation therapy; Image-guided radiotherapy; Lymphoma.
Conflict of interest statement
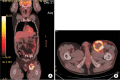
Figures




References
-
- Verellen D, De Ridder M, Storme G. A (short) history of image-guided radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2008;86:4–13. - PubMed
-
- Dawson LA, Jaffray DA. Advances in image-guided radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:938–946. - PubMed
-
- Michalski J, Purdy JA, Gaspar L, et al. Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. Research Plan 2002-2006. Image-Guided Radiation Therapy Committee. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51(3 Suppl 2):60–65. - PubMed
-
- Das S, Liu T, Jani AB, et al. Comparison of image-guided radiotherapy technologies for prostate cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 2014;37:616–623. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous