The Direct Interaction between Two Morphogenetic Proteins Is Essential for Spore Coat Formation in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 26484546
- PMCID: PMC4618286
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141040
The Direct Interaction between Two Morphogenetic Proteins Is Essential for Spore Coat Formation in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
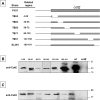
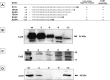
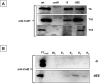
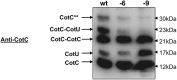
In Bacillus subtilis the protective layers that surround the mature spore are formed by over seventy different proteins. Some of those proteins have a regulatory role on the assembly of other coat proteins and are referred to as morphogenetic factors. CotE is a major morphogenetic factor, known to form a ring around the forming spore and organize the deposition of the outer surface layers. CotH is a CotE-dependent protein known to control the assembly of at least nine other coat proteins. We report that CotH also controls the assembly of CotE and that this mutual dependency is due to a direct interaction between the two proteins. The C-terminal end of CotE is essential for this direct interaction and CotH cannot bind to mutant CotE deleted of six or nine C-terminal amino acids. However, addition of a negatively charged amino acid to those deleted versions of CotE rescues the interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Flexibility of the programme of spore coat formation in Bacillus subtilis: bypass of CotE requirement by over-production of CotH.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 27;8(9):e74949. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074949. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24086406 Free PMC article.
-
Morphogenesis of the Bacillus anthracis spore.J Bacteriol. 2007 Feb;189(3):691-705. doi: 10.1128/JB.00921-06. Epub 2006 Nov 17. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17114257 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the Bacillus subtilis morphogenetic spore coat protein CotE.Mol Microbiol. 2001 Nov;42(4):1107-20. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02708.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11737650
-
Exploring the interaction network of the Bacillus subtilis outer coat and crust proteins.Microbiol Res. 2017 Nov;204:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.08.004. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Microbiol Res. 2017. PMID: 28870294
-
Bacillus subtilis spore coat.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999 Mar;63(1):1-20. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.63.1.1-20.1999. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10066829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in research and application development of surface display technology using Bacillus subtilis spores.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Mar;104(6):2319-2331. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10348-x. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31989224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A protein phosphorylation module patterns the Bacillus subtilis spore outer coat.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Dec;114(6):934-951. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14562. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32592201 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics as an Alternative to Antibiotics: Genomic and Physiological Characterization of Aerobic Spore Formers from the Human Intestine.Microorganisms. 2023 Jul 31;11(8):1978. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11081978. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37630538 Free PMC article.
-
CotG Mediates Spore Surface Permeability in Bacillus subtilis.mBio. 2022 Dec 20;13(6):e0276022. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02760-22. Epub 2022 Nov 10. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36354330 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Spore-Based Delivery System: 20 Years of a Versatile Approach for Innovative Vaccines.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 6;13(6):947. doi: 10.3390/biom13060947. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371527 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Losick R, Youngman P, Piggot PJ. Genetics of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis . Ann. Rev. Genet. 1986; 20:625–669. - PubMed
-
- Stragier P, Losick R. Molecular genetics of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis . Ann. Rev. Genet. 1996; 30:297–241. - PubMed
-
- Setlow P. Spores of Bacillus subtilis: their resistance to and killing by radiation, heat and chemicals. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006; 101:514–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

