VHL-dependent alterations in the secretome of renal cell carcinoma: Association with immune cell response?
- PMID: 26486078
- PMCID: PMC4791241
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5560
VHL-dependent alterations in the secretome of renal cell carcinoma: Association with immune cell response?
Abstract
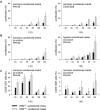
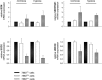
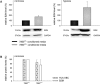
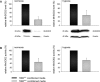
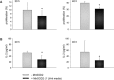
Secreted proteins could modulate the interaction between tumor, stroma and immune cells within the tumor microenvironment thereby mounting an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. In order to determine the secretome-mediated, von Hippel Lindau (VHL)-regulated cross-talk between tumor cells and T lymphocytes peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from healthy donors were either cultured in conditioned media obtained from normoxic and hypoxic human VHL-deficient renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cell line (786-0VHL-) and its wild type (wt) VHL-transfected counterpart (786-0VHL+) or directly co-cultured with both cell lines. An increased T cell proliferation was detected in the presence of 786-0VHL+-conditioned medium. By applying a quantitative proteomic-based approach using differential gel electrophoresis followed by mass spectrometry fourteen proteins were identified to be differentially expressed within the secretome of 786-0VHL- cells when compared to that of 786-0VHL+ cells. All proteins identified were involved in multiple tumor-associated biological functions including immune responses. Functional studies on manganese superoxide dismutase 2 (MnSOD2) demonstrated that it was a regulator of T cell activation-induced oxidative signaling and cell death. Direct effects of soluble MnSOD2 on the growth properties and interleukin 2 (IL-2) secretion of T cells could be demonstrated underlining the critical role of extracellular MnSOD2 levels for T cell proliferation and activation.
Keywords: VHL; manganese superoxide dismutase 2; renal cell carcinoma; secretome; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Distinct von Hippel-Lindau gene and hypoxia-regulated alterations in gene and protein expression patterns of renal cell carcinoma and their effects on metabolism.Oncotarget. 2015 May 10;6(13):11395-406. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3456. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25890500 Free PMC article.
-
Mutated Von Hippel-Lindau-renal cell carcinoma (RCC) promotes patients specific natural killer (NK) cytotoxicity.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Dec 4;37(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0952-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30514329 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic identification of a role for the von Hippel Lindau tumour suppressor in changes in the expression of mitochondrial proteins and septin 2 in renal cell carcinoma.Proteomics. 2006 Jul;6(13):3880-93. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200500811. Proteomics. 2006. PMID: 16739133
-
The Role of the Lymphocyte Functional Crosstalk and Regulation in the Context of Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment-Review.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 6;10:2043. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02043. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31555274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Migrating into the Tumor: a Roadmap for T Cells.Trends Cancer. 2017 Nov;3(11):797-808. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.09.006. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Trends Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29120755 Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating SOD2 Is a Candidate Response Biomarker for Neoadjuvant Therapy in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 10;14(16):3858. doi: 10.3390/cancers14163858. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010852 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of immunity and inflammation by hypoxia in immunological niches.Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 Dec;17(12):774-785. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.103. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28972206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth-induced stress enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by IL-6 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma via the Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway.Oncogenesis. 2017 Aug 28;6(8):e375. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2017.74. Oncogenesis. 2017. PMID: 28846080 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated reprogramming of renal cancer transcriptome, metabolome and secretome associates with immune tumor infiltration.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Jan 5;23(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02845-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 36604669 Free PMC article.
-
Culture in embryonic kidney serum and xeno-free media as renal cell carcinoma and renal cell carcinoma cancer stem cells research model.Cytotechnology. 2018 Apr;70(2):761-782. doi: 10.1007/s10616-017-0181-5. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Cytotechnology. 2018. PMID: 29455394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ning H, Shao QQ, Ding KJ, Gao DX, Lu QL, Cao QW, Niu ZH, Fu Q, Zhang CH, Qu X, Lu JJ. Tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells are positively correlated with angiogenic status in renal cell carcinoma. Chinese medical journal. 2012;125:2120–2125. - PubMed
-
- Sell K, Barth PJ, Moll R, Thomas MA, Zimmer N, Oplesch E, Gudo M, Schrader M, Hofmann R, Schrader AJ. Localization of FOXP3-positive cells in renal cell carcinoma. Tumour biology: the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine. 2012;33:507–513. - PubMed
-
- Santoni M, Berardi R, Amantini C, Burattini L, Santini D, Santoni G, Cascinu S. Role of natural and adaptive immunity in renal cell carcinoma response to VEGFR-TKIs and mTOR inhibitor. International journal of cancer Journal international du cancer. 2014;134:2772–2777. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

