Detection of canonical A-to-G editing events at 3' UTRs and microRNA target sites in human lungs using next-generation sequencing
- PMID: 26486088
- PMCID: PMC4742137
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6132
Detection of canonical A-to-G editing events at 3' UTRs and microRNA target sites in human lungs using next-generation sequencing
Abstract
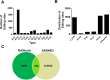
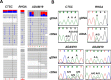
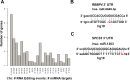
RNA editing is a post-transcriptional modification of RNA. The majority of these changes result from adenosine deaminase acting on RNA (ADARs) catalyzing the conversion of adenosine residues to inosine in double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs). Massively parallel sequencing has enabled the identification of RNA editing sites in human transcriptomes. In this study, we sequenced DNA and RNA from human lungs and identified RNA editing sites with high confidence via a computational pipeline utilizing stringent analysis thresholds. We identified a total of 3,447 editing sites that overlapped in three human lung samples, and with 50% of these sites having canonical A-to-G base changes. Approximately 27% of the edited sites overlapped with Alu repeats, and showed A-to-G clustering (>3 clusters in 100 bp). The majority of edited sites mapped to either 3' untranslated regions (UTRs) or introns close to splice sites; whereas, only few sites were in exons resulting in non-synonymous amino acid changes. Interestingly, we identified 652 A-to-G editing events in the 3' UTR of 205 target genes that mapped to 932 potential miRNA target binding sites. Several of these miRNA edited sites were validated in silico. Additionally, we validated several A-to-G edited sites by Sanger sequencing. Altogether, our study suggests a role for RNA editing in miRNA-mediated gene regulation and splicing in human lungs. In this study, we have generated a RNA editome of human lung tissue that can be compared with other RNA editomes across different lung tissues to delineate a role for RNA editing in normal and diseased states.
Keywords: 3’UTRs; RNA editing; RNA-seq; exome; microRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noncoding regions of C. elegans mRNA undergo selective adenosine to inosine deamination and contain a small number of editing sites per transcript.RNA Biol. 2015;12(2):162-74. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1017220. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 25826568 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of widespread ultra-edited human RNAs.PLoS Genet. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002317. Epub 2011 Oct 20. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22028664 Free PMC article.
-
RNA editing of non-coding RNA and its role in gene regulation.Biochimie. 2015 Oct;117:22-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.05.020. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 26051678 Review.
-
Combinatory RNA-Sequencing Analyses Reveal a Dual Mode of Gene Regulation by ADAR1 in Gastric Cancer.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Jul;63(7):1835-1850. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5081-9. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29691780
-
A-to-I editing of coding and non-coding RNAs by ADARs.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Feb;17(2):83-96. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2015.4. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26648264 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ADAR2 regulates RNA stability by modifying access of decay-promoting RNA-binding proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Apr 20;45(7):4189-4201. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1304. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28053121 Free PMC article.
-
RNA editing alterations define manifestation of prion diseases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Sep 24;116(39):19727-19735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803521116. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31492812 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of consistently RNA edited sites in human blood reveals interactions with mRNA processing genes and suggests correlations with cell types and biological variables.BMC Genomics. 2018 Dec 27;19(1):963. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5364-8. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30587120 Free PMC article.
-
ADAR Mediated RNA Editing Modulates MicroRNA Targeting in Human Breast Cancer.Processes (Basel). 2018 May;6(5):42. doi: 10.3390/pr6050042. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Processes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30197877 Free PMC article.
-
ncRNA Editing: Functional Characterization and Computational Resources.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2883:455-495. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4290-0_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39702721
References
-
- Benne R, Van den Burg J, Brakenhoff JP, Sloof P, Van Boom JH, Tromp MC. Major transcript of the frameshifted coxII gene from trypanosome mitochondria contains four nucleotides that are not encoded in the DNA. Cell. 1986;46:819–826. - PubMed
-
- Powell LM, Wallis SC, Pease RJ, Edwards YH, Knott TJ, Scott J. A novel form of tissue-specific RNA processing produces apolipoprotein-B48 in intestine. Cell. 1987;50:831–840. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton CE, Papavasiliou FN, Rosenberg BR. Diverse functions for DNA and RNA editing in the immune system. RNA biology. 2010;7:220–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

