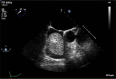
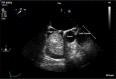
Cardiac lipoma
- PMID: 26486106
- PMCID: PMC4612478
- DOI: 10.3402/jchimp.v5.28449
Cardiac lipoma
Abstract
Lipomas of the heart are encapsulated tumors that are composed primarily of mature fat cells. Cardiac lipomas can originate either from subendocardium (approximately 50%), subpericardium (25%), or from the myocardium (25%) and may be located more frequently in left ventricle or right atrium. We report a 74-year-old female who presented with dyspnea on exertion and was found to have 5×5 cm mass occupying most of the right atrium on a transesophageal echocardiogram.
Keywords: TEE; cardiac; dyspnea; lipoma.
Figures
References
-
- McAllister HA., Jr. Tumors of the heart and pericardium. In: Silver MD, editor. Cardiovascular pathology. 2nd ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1991. pp. 1297–333.
-
- Colucci WS, Schoen FJ, Braunwald E. Primary tumors of the heart. In: Braunwald E, editor. Heart disease: a textbook of cardiovascular medicine. Vol. 2. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders; 1997. pp. 1464–77.
-
- McAllister HA, Fenoglio JJ. Tumors of the cardiovascular system – atlas of tumor pathology. 2nd series. Washington, DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 1978.
-
- Hananouchi GI, Goff WB. Cardiac lipoma: six-year follow-up with MRI characteristics, and a review of the literature. Magn Reson Imaging. 1990;8(6):825–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources