Auricular vagal nerve stimulation ameliorates burn-induced gastric dysmotility via sympathetic-COX-2 pathways in rats
- PMID: 26486522
- PMCID: PMC4688125
- DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12693
Auricular vagal nerve stimulation ameliorates burn-induced gastric dysmotility via sympathetic-COX-2 pathways in rats
Abstract
Background: Severe burn injury has been demonstrated to delay gastric emptying. The aim of this study was to investigate effects and cellular mechanisms of auricular electroacupuncture (AEA) at the acupoints innervated by the auricular branch of vagus nerve on burn-induced gastric dysmotility in rats.
Methods: Propranolol (β-adrenoceptor antagonist) was injected intraperitoneally after the rats underwent burn injury. All experiments were performed 6 h following burn/sham burn injury. AEA was performed at bilateral auricular acupoints for 45 min. Electrocardiogram was recorded for 30 min. Plasma hormones were measured; cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expressions in gastric tissue were measured using western blotting and real-time RT-PCR.
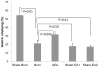
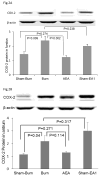
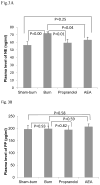
Key results: (i) Burn injury delayed gastric emptying (p = 0.006) and AEA increased gastric emptying by 49% (p = 0.045). (ii) Burn injury evoked a significant elevation in plasma noradrenaline, which was suppressed by AEA. (iii) Burn injury significantly increased protein and mRNA expressions of COX-2 in gastric fundus and antrum. AEA suppressed burn-induced increase in protein expressions, but not mRNA expressions of COX-2.
Conclusions & inferences: Burn injury delays gastric emptying by up-regulating COX-2 attributed to sympathetic overactivity. AEA improves burn-induced delay in gastric emptying, possibly mediated via the sympathetic-COX-2 pathway.
Keywords: COX-2; auricular electroacupuncture; autonomic function; gastric emptying; vagal nerve stimulation.
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture improves burn-induced impairment in gastric motility mediated via the vagal mechanism in rats.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013 Oct;25(10):807-e635. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12183. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013. PMID: 23848593
-
Autonomic-cyclooxygenase-2 Mechanisms of Electroacupuncture on Thermal Injury-induced Gastric Dysmotility in Rats.J Transl Gastroenterol. 2024 Jul-Sep;2(3):139-149. doi: 10.14218/jtg.2024.00026. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Transl Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 40666705 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and mechanisms of auricular electroacupuncture on gastric hypersensitivity in a rodent model of functional dyspepsia.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 28;12(3):e0174568. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174568. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28350818 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of gastric paralysis after gastric schwannoma by electroacupuncture: A case report and literature review.Explore (NY). 2024 Jul-Aug;20(4):592-596. doi: 10.1016/j.explore.2023.11.009. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Explore (NY). 2024. PMID: 38008591 Review.
-
P-Stim auricular electroacupuncture stimulation device for pain relief.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2007 Jan;4(1):23-32. doi: 10.1586/17434440.4.1.23. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2007. PMID: 17187468 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Directions in the Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation I - A Physiological Perspective.Front Neurosci. 2019 Aug 9;13:854. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00854. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31447643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: an innovative strategy for treating diseases.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 4;52(1):199. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10288-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39903351 Review.
-
Transcutaneous auricular vagal nerve stimulation improves functional dyspepsia by enhancing vagal efferent activity.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):G700-G711. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00426.2020. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33624527 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Mechano-Transcription Process as Therapeutic Intervention in Gastrointestinal Disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 21;12:809350. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.809350. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34992543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Response in Rats following Electroacupuncture or Moxibustion Stimulation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 May 2;2019:6947471. doi: 10.1155/2019/6947471. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31186665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oliveira HM, Sallam HS, Espana-Tenorio J, et al. Gastric and small bowel ileus after severe burn in rats: the effect of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Burns. 2009;35:1180–1184. - PubMed
-
- Sallam HS, Oliveira HM, Liu S, Chen JD. Mechanisms of burn-induced impairment in gastric slow waves and emptying in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010;299:R298–305. - PubMed
-
- Khorasani EN, Mansouri F. Effect of early enteral nutrition on morbidity and mortality in children with burns. Burns. 2010;36:1067–1071. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

