Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Causes Multiple Organ Damage and Lethal Disease in Mice Transgenic for Human Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4
- PMID: 26486634
- PMCID: PMC4747621
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiv499
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Causes Multiple Organ Damage and Lethal Disease in Mice Transgenic for Human Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4
Abstract
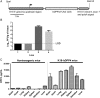
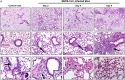
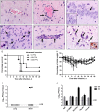
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) causes life-threatening disease. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) is the receptor for cell binding and entry. There is a need for small-animal models of MERS, but mice are not susceptible to MERS because murine dpp4 does not serve as a receptor. We developed transgenic mice expressing human DPP4 (hDPP4) under the control of the surfactant protein C promoter or cytokeratin 18 promoter that are susceptible to infection with MERS-CoV. Notably, mice expressing hDPP4 with the cytokeratin 18 promoter developed progressive, uniformly fatal disease following intranasal inoculation. High virus titers were present in lung and brain tissues 2 and 6 days after infection, respectively. MERS-CoV-infected lungs revealed mononuclear cell infiltration, alveolar edema, and microvascular thrombosis, with airways generally unaffected. Brain disease was observed, with the greatest involvement noted in the thalamus and brain stem. Animals immunized with a vaccine candidate were uniformly protected from lethal infection. These new mouse models of MERS-CoV should be useful for investigation of early disease mechanisms and therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: DPP4/CD26; MERS; transgenic mice.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med 2012; 367:1814–20. - PubMed
-
- Arabi YM, Arifi AA, Balkhy HH et al. . Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. Ann Intern Med 2014; 160:389–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

