Comparison among three variant callers and assessment of the accuracy of imputation from SNP array data to whole-genome sequence level in chicken
- PMID: 26486989
- PMCID: PMC4618161
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-2059-2
Comparison among three variant callers and assessment of the accuracy of imputation from SNP array data to whole-genome sequence level in chicken
Abstract
Background: The technical progress in the last decade has made it possible to sequence millions of DNA reads in a relatively short time frame. Several variant callers based on different algorithms have emerged and have made it possible to extract single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) out of the whole-genome sequence. Often, only a few individuals of a population are sequenced completely and imputation is used to obtain genotypes for all sequence-based SNP loci for other individuals, which have been genotyped for a subset of SNPs using a genotyping array.
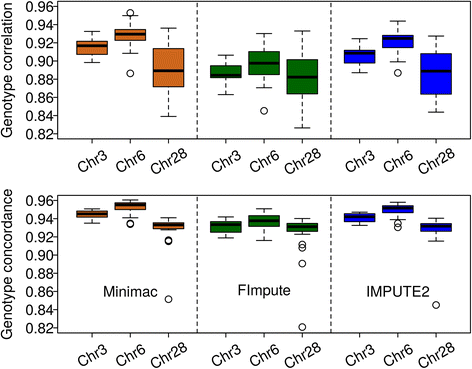
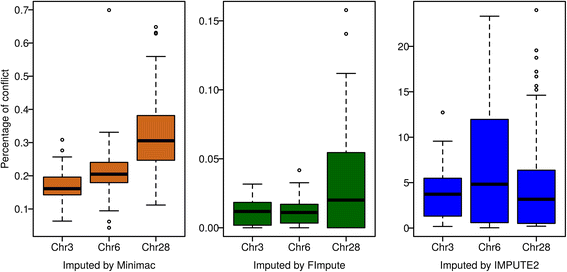
Methods: First, we compared the sets of variants detected with different variant callers, namely GATK, freebayes and SAMtools, and checked the quality of genotypes of the called variants in a set of 50 fully sequenced white and brown layers. Second, we assessed the imputation accuracy (measured as the correlation between imputed and true genotype per SNP and per individual, and genotype conflict between father-progeny pairs) when imputing from high density SNP array data to whole-genome sequence using data from around 1000 individuals from six different generations. Three different imputation programs (Minimac, FImpute and IMPUTE2) were checked in different validation scenarios.
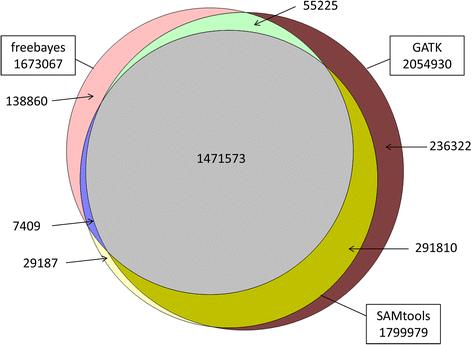
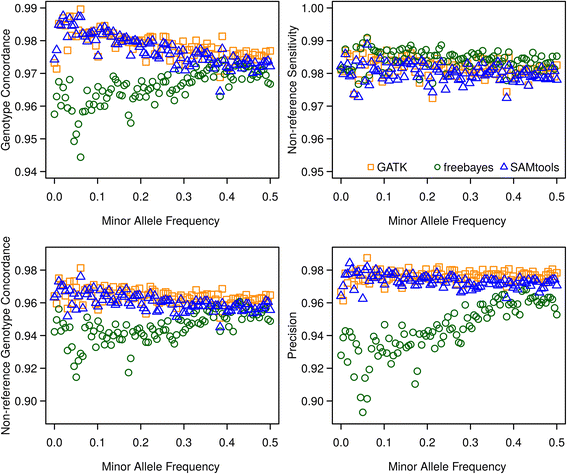
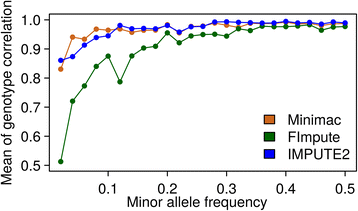
Results: There were 1,741,573 SNPs detected by all three callers on the studied chromosomes 3, 6, and 28, which was 71.6 % (81.6 %, 88.0 %) of SNPs detected by GATK (SAMtools, freebayes) in total. Genotype concordance (GC) defined as the proportion of individuals whose array-derived genotypes are the same as the sequence-derived genotypes over all non-missing SNPs on the array were 0.98 (GATK), 0.97 (freebayes) and 0.98 (SAMtools). Furthermore, the percentage of variants that had high values (>0.9) for another three measures (non-reference sensitivity, non-reference genotype concordance and precision) were 90 (88, 75) for GATK (SAMtools, freebayes). With all imputation programs, correlation between original and imputed genotypes was >0.95 on average with randomly masked 1000 SNPs from the SNP array and >0.85 for a leave-one-out cross-validation within sequenced individuals.
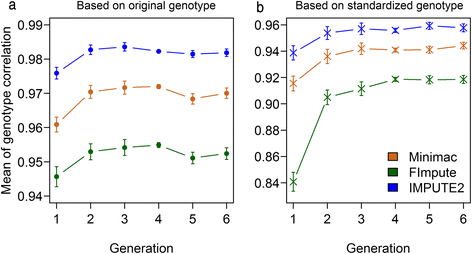
Conclusions: Performance of all variant callers studied was very good in general, particularly for GATK and SAMtools. FImpute performed slightly worse than Minimac and IMPUTE2 in terms of genotype correlation, especially for SNPs with low minor allele frequency, while it had lowest numbers in Mendelian conflicts in available father-progeny pairs. Correlations of real and imputed genotypes remained constantly high even if individuals to be imputed were several generations away from the sequenced individuals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the accuracy of imputed sequence variant genotypes and their utility for causal variant detection in cattle.Genet Sel Evol. 2017 Feb 21;49(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12711-017-0301-x. Genet Sel Evol. 2017. PMID: 28222685 Free PMC article.
-
Low-depth genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) in a bovine population: strategies to maximize the selection of high quality genotypes and the accuracy of imputation.BMC Genet. 2017 Apr 5;18(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12863-017-0501-y. BMC Genet. 2017. PMID: 28381212 Free PMC article.
-
Imputation of sequence level genotypes in the Franches-Montagnes horse breed.Genet Sel Evol. 2014 Oct 1;46(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12711-014-0063-7. Genet Sel Evol. 2014. PMID: 25927638 Free PMC article.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Identification in Polyploids: A Review, Example, and Recommendations.Mol Plant. 2015 Jun;8(6):831-46. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Mol Plant. 2015. PMID: 25676455 Review.
-
Evaluation of measures of correctness of genotype imputation in the context of genomic prediction: a review of livestock applications.Animal. 2014 Nov;8(11):1743-53. doi: 10.1017/S1751731114001803. Epub 2014 Jul 21. Animal. 2014. PMID: 25045914 Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-analyses of genome wide association studies in lines of laying hens divergently selected for feather pecking using imputed sequence level genotypes.BMC Genet. 2020 Oct 1;21(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s12863-020-00920-9. BMC Genet. 2020. PMID: 33004014 Free PMC article.
-
GWAS on Imputed Whole-Genome Resequencing From Genotyping-by-Sequencing Data for Farrowing Interval of Different Parities in Pigs.Front Genet. 2019 Oct 18;10:1012. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01012. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31681435 Free PMC article.
-
A high-throughput SNP discovery strategy for RNA-seq data.BMC Genomics. 2019 Feb 27;20(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5533-4. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30813897 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Age-Specific and Common Key Regulatory Mechanisms Governing Eggshell Strength in Chicken Using Random Forests.Genes (Basel). 2020 Apr 24;11(4):464. doi: 10.3390/genes11040464. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32344666 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic analysis for virulence determinants in feline herpesvirus type-1 isolates.Virus Genes. 2020 Feb;56(1):49-57. doi: 10.1007/s11262-019-01718-3. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Virus Genes. 2020. PMID: 31776852 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

