A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Outcomes of Pregnancy in CKD and CKD Outcomes in Pregnancy
- PMID: 26487769
- PMCID: PMC4633792
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.09250914
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Outcomes of Pregnancy in CKD and CKD Outcomes in Pregnancy
Abstract
Background and objectives: We undertook a systematic review and meta-analysis of published cohort studies and case-control studies to estimate (1) the risk of pregnancy complications among patients with CKD versus those without CKD and (2) the risk of CKD progression among pregnant patients versus nonpregnant controls with CKD.
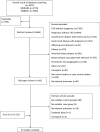
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We searched electronic databases for studies published between 1946 and 2014, and we reviewed articles using validity criteria. Random-effects analytical methods were used.
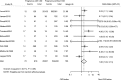
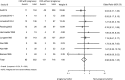
Results: Twenty-three studies (14 with data for adverse pregnancy outcomes and 9 for renal outcomes) with 506,340 pregnancies were included. Pregnancy with CKD had greater odds of preeclampsia (odds ratio [OR], 10.36; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 6.28 to 17.09), premature delivery (OR, 5.72; 95% CI, 3.26 to 10.03), small for gestational age/low birth weight (OR, 4.85; 95% CI, 3.03 to 7.76), cesarean section (OR, 2.67; 95% CI, 2.01 to 3.54), and failure of pregnancy (OR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.03 to 3.13). Subgroup analysis showed that odds of preeclampsia (P<0.01) and premature delivery (P<0.01) were higher in women with nondiabetic nephropathy compared with diabetic nephropathy, and the odds of preeclampsia (P=0.01) and premature delivery (P<0.01) were higher in women with macroproteinuria compared with microproteinuria. The median for follow-up time for renal events was 5 years (interquartile range, 5-14.7 years). There were no significant differences in the occurrence of renal events between CKD pregnant women and those without pregnancy (OR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.69 to 1.35). Subgroup analysis showed that publication year, sample size, follow-up years, type of primary disease, CKD classification, level of serum creatinine at baseline, proteinuria, and level of systolic BP did not modify the renal outcomes.
Conclusions: The risks of adverse maternal and fetal outcomes in pregnancy are higher for women with CKD versus pregnant women without CKD. However, pregnancy was not a risk factor for progression of renal disease in women with CKD before pregnancy.
Keywords: cesarean section; chronic kidney disease; follow-up studies; gestational age; humans; infant; low birth weight; pre-eclampsia; pregnancy; premature birth; renal function.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures




References
-
- Chadban SJ, Briganti EM, Kerr PG, Dunstan DW, Welborn TA, Zimmet PZ, Atkins RC: Prevalence of kidney damage in Australian adults: The AusDiab kidney study. J Am Soc Nephrol 14[Suppl 2]: S131–S138, 2003 - PubMed
-
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.htm. Accessed September 22 2010
-
- Zhang L, Wang F, Wang L, Wang W, Liu B, Liu J, Chen M, He Q, Liao Y, Yu X, Chen N, Zhang JE, Hu Z, Liu F, Hong D, Ma L, Liu H, Zhou X, Chen J, Pan L, Chen W, Wang W, Li X, Wang H: Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: A cross-sectional survey. Lancet 379: 815–822, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Hou S: Historical perspective of pregnancy in chronic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 14: 116–118, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Vidaeff AC, Yeomans ER, Ramin SM: Pregnancy in women with renal disease. Part I: General principles. Am J Perinatol 25: 385–397, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

