Heparan sulfate proteoglycans: a sugar code for vertebrate development?
- PMID: 26487777
- PMCID: PMC4631762
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.098178
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans: a sugar code for vertebrate development?
Abstract
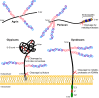
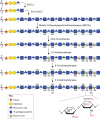
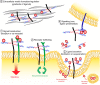
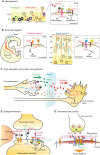
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) have long been implicated in a wide range of cell-cell signaling and cell-matrix interactions, both in vitro and in vivo in invertebrate models. Although many of the genes that encode HSPG core proteins and the biosynthetic enzymes that generate and modify HSPG sugar chains have not yet been analyzed by genetics in vertebrates, recent studies have shown that HSPGs do indeed mediate a wide range of functions in early vertebrate development, for example during left-right patterning and in cardiovascular and neural development. Here, we provide a comprehensive overview of the various roles of HSPGs in these systems and explore the concept of an instructive heparan sulfate sugar code for modulating vertebrate development.
Keywords: Glycan; Heart; Left/right asymmetry; Nervous system; Patterning; Sugars.
© 2015. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analyzing the Role of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans in Axon Guidance In Vivo in Zebrafish.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2303:427-442. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1398-6_34. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34626398
-
Combinatorial roles of heparan sulfate proteoglycans and heparan sulfates in Caenorhabditis elegans neural development.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 23;9(7):e102919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102919. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25054285 Free PMC article.
-
A network of HSPG core proteins and HS modifying enzymes regulates netrin-dependent guidance of D-type motor neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 16;8(9):e74908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074908. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24066155 Free PMC article.
-
Coreceptor functions of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 May 1;322(5):C896-C912. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00050.2022. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35319900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of the Biosynthesis & Enzymatic Modification of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans: Implications for Tumorigenesis and Cancer Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 26;18(7):1361. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071361. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28672878 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The exostosin glycosyltransferase 1/STAT3 axis is a driver of breast cancer aggressiveness.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jan 16;121(3):e2316733121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2316733121. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38215181 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational analysis of genes with ureteric progenitor cell-specific expression in branching morphogenesis of the mouse kidney.Dev Dyn. 2020 Jun;249(6):765-774. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.157. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Dev Dyn. 2020. PMID: 32017326 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Sulf1 is required for the termination of intestinal stem cell division during regeneration.J Cell Sci. 2017 Jan 15;130(2):332-343. doi: 10.1242/jcs.195305. Epub 2016 Nov 25. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 27888216 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of glycosaminoglycans as regulators of ligand/receptor complexes.Open Biol. 2018 Oct 3;8(10):180026. doi: 10.1098/rsob.180026. Open Biol. 2018. PMID: 30282658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene-Interaction-Sensitive enrichment analysis in congenital heart disease.BioData Min. 2022 Feb 12;15(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13040-022-00287-w. BioData Min. 2022. PMID: 35151364 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

