Exercise preconditioning exhibits neuroprotective effects on hippocampal CA1 neuronal damage after cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 26487851
- PMCID: PMC4590236
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.162756
Exercise preconditioning exhibits neuroprotective effects on hippocampal CA1 neuronal damage after cerebral ischemia
Abstract
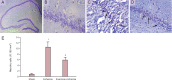
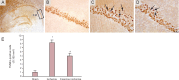
Recent evidence has suggested the neuroprotective effects of physical exercise on cerebral ischemic injury. However, the role of physical exercise in cerebral ischemia-induced hippocampal damage remains controversial. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effects of pre-ischemia treadmill training on hippocampal CA1 neuronal damage after cerebral ischemia. Male adult rats were randomly divided into control, ischemia and exercise + ischemia groups. In the exercise + ischemia group, rats were subjected to running on a treadmill in a designated time schedule (5 days per week for 4 weeks). Then rats underwent cerebral ischemia induction through occlusion of common carotids followed by reperfusion. At 4 days after cerebral ischemia, rat learning and memory abilities were evaluated using passive avoidance memory test and rat hippocampal neuronal damage was detected using Nissl and TUNEL staining. Pre-ischemic exercise significantly reduced the number of TUNEL-positive cells and necrotic cell death in the hippocampal CA1 region as compared to the ischemia group. Moreover, pre-ischemic exercise significantly prevented ischemia-induced memory dysfunction. Pre-ischemic exercise mighct prevent memory deficits after cerebral ischemia through rescuing hippocampal CA1 neurons from ischemia-induced degeneration.
Keywords: Nissl staining; TUNEL; apoptosis; cerebral ischemia; hippocampus; memory; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration; physical exercise.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
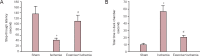
Similar articles
-
Preconditioning exercise reduces hippocampal neuronal damage via increasing Klotho expression in ischemic rats.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Oct 1;188:133-142. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.07.022. Epub 2022 Jul 30. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 35918034
-
Ischemic tolerance to memory impairment associated with hippocampal neuronal damage after transient cerebral ischemia in rats.Brain Res Bull. 1996;40(3):229-36. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(96)00050-0. Brain Res Bull. 1996. PMID: 8736585
-
Protection of Hippocampal CA1 Neurons Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Exercise Preconditioning via Modulation of Bax/Bcl-2 Ratio and Prevention of Caspase-3 Activation.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2016 Jan;7(1):21-9. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27303596 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral Ischemia [Internet].Brisbane (AU): Exon Publications; 2021 Nov 6. Brisbane (AU): Exon Publications; 2021 Nov 6. PMID: 34905305 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Therapeutic physical exercise in neural injury: friend or foe?J Phys Ther Sci. 2015 Dec;27(12):3933-5. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.3933. Epub 2015 Dec 28. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015. PMID: 26834383 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sulfur dioxide reduces hippocampal cell death and improves learning and memory deficits in a rat model of transient global ischemia/reperfusion.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Oct;21(10):998-1003. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2018.29404.7106. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30524672 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise preconditioning attenuates cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal apoptosis, Th17/Treg imbalance, and inflammation in rats by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.Brain Behav. 2023 Jun;13(6):e3030. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3030. Epub 2023 May 4. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 37143406 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise preconditioning mitigates brain injury after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by restraining TIMP1.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Oct;12(10):e70008. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70008. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39364701 Free PMC article.
-
Insight Into the Mechanism of Exercise Preconditioning in Ischemic Stroke.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 8;13:866360. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.866360. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35350755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective potential of exercise preconditioning in stroke.Cond Med. 2017;1(1):27-34. Cond Med. 2017. PMID: 30465042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aboutaleb N, Kalalianmoghaddam H, Eftekhari S, Shahbazi A, Abbaspour H, Khaksari M. Apelin-13 inhibits apoptosis of cortical neurons following brain ischemic reperfusion injury in a transient model of focal cerebral ischemia. Int J Pept Res Ther. 2014;20:127–132.
-
- Ang E, Wong P, Moochhala S, Ng Y. Neuroprotection associated with running: is it a result of increased endogenous neurotrophic factors? Neuroscience. 2003;118:335–345. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch T, Schönfeld R, Müller F, Alfke K, Leplow B, Aldenhoff J, Deuschl G, Koch J. Focal lesions of human hippocampal CA1 neurons in transient global amnesia impair place memory. Science. 2010;328:1412–1415. - PubMed
-
- Chan PH. Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21:2–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
