Lamivudine Resistance and Precore Variants in Iranian Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B: Correlation With Virological and Clinical Features
- PMID: 26487918
- PMCID: PMC4609034
- DOI: 10.5812/jjm.20262
Lamivudine Resistance and Precore Variants in Iranian Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B: Correlation With Virological and Clinical Features
Abstract
Background: Long-term lamivudine therapy, despite its initial effectiveness against hepatitis B virus (HBV), is associated with the emergence of drug resistance mutations in polymerase protein.
Objectives: The aim of the present study was to determine the prevalence of precore and lamivudine drug resistance mutations in lamivudine treated patients with chronic B hepatitis.
Patients and methods: Sequential sera were obtained from 88 chronic HBV carriers who received lamivudine for more than 24 months. Polymerase and precore regions were directly sequenced for these groups: I (before treatment), II, and III (12 and 24 months after treatment, respectively).
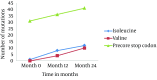
Results: All patients (100%) were contained genotype D, subtype ayw2. One (1.1%), 12 (13.6%), and 22 (25%) members of groups I, II, and III had the replacement of either isoleucine or valine instead of methionine in tyrosine-methionine-aspartate-aspartate (YMDD) motif, respectively. The frequency of mutations from 0 time point to 12 and 24 months showed that there was an increasing trend between sequential samples (P < 0.001). In group I, 31 (35.2%); II, 36 (41.0%) and III, 41 (46.6%) members had the precore stop codon mutations. The frequency of mutations from 0 time point to 12 and 24 months showed that there was an ascending trend between sequential samples. Indeed, frequency of precore stop codon was significantly increased with the passage of time (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Presence of drug resistance mutations among the patients was significant. Precore mutations were common amongst Iranian HBV chronic carriers under lamivudine therapy and these mutations were accompanied by clinical relapse.
Keywords: Lamivudine; Mutations; Therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evolution of viral load and changes of polymerase and precore/core promoter sequences in lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus during adefovir therapy.J Med Virol. 2007 Jul;79(7):902-10. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20819. J Med Virol. 2007. PMID: 17516533
-
Correlation of the occurrence of YMDD mutations with HBV genotypes, HBV-DNA levels, and HBeAg status in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B during lamivudine treatment.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2012 Apr;11(2):172-6. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(12)60144-1. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2012. PMID: 22484586
-
Differences of YMDD mutational patterns, precore/core promoter mutations, serum HBV DNA levels in lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B genotypes B and C.J Viral Hepat. 2007 Nov;14(11):767-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2007.00869.x. J Viral Hepat. 2007. PMID: 17927612
-
Current pharmacotherapy for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2003 Oct;4(10):1821-7. doi: 10.1517/14656566.4.10.1821. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2003. PMID: 14521491 Review.
-
Management of YMDD mutations during lamivudine therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002 Dec;17 Suppl 3:S333-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.17.s3.23.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002. PMID: 12472959 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources