Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 microspheres for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 26487939
- PMCID: PMC4570909
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2015.056
Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 microspheres for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is aggressive primary malignancy of the liver that most commonly presents late in the disease course. As a result, the majority of patients are not candidates for curative therapies. Locoregional therapies including Yttrium-90 (Y-90) radioembolization play an important role in management of the vast majority of patients with HCC.
Methods: Patients with unnresectable HCC (n=17) treated with Y-90 radioembolization from 2005 to 2014 were evaluated retrospectively. Data was abstracted from medical records including patient charts, laboratory data, and imaging. Toxicities were recorded using Common Terminology Criteria 3.0. Response was recorded according to modified RECIST (mRECIST) criteria.
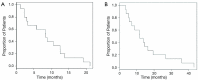
Results: Seventeen patients received 33 treatments with Y-90 radioembolization. A majority (65%) received TheraSphere with a minority (35%) receiving SIR-Spheres. The median treatment activity delivered was 1.725 gBq (range, 1.4-2.5 gBq). The median treatment dose delivered was 100 Gy (range, 90-120 Gy). The median lung shunt fraction was 2.02% (range, 1.5-4.1%). The most common clinical toxicity among all patients was nausea and vomiting (59%), primarily grade 1 and 2. Other post-treatment findings included abdominal pain (29%), fatigue (53%), and weight loss (18%). One patient developed a grade 5 gastric ulcer after the treatment. A clinical benefit, defined as patients achieving complete response (CR), partial response (PR) or stable disease (SD), was seen in 48% of patients. PR was seen in 24% of cases; progressive disease (PD) was noted in 35%. Patients survived for a median of 8.4 months (range, 1.3 to 21.1 months) after the first radioembolization treatment. Median survival after Y-90 treatment was 8.4 months among patients treated TheraSphere as compared with 7.8 months in patients treated with SIR-Spheres. The mean overall survival from the time of diagnosis was 11.7 months (range, 3.4 to 43.2 months).
Conclusions: For patients with unresectable HCC, Y-90 radioembolization is a safe and well-tolerated procedure. Our experience suggests that a significant percentage of patients achieve clinical benefit including many with PR. Survival after treatment from this single-center, transplant center is in line with prior reports. Prospective, randomized data is required to compare radioembolization with other therapies including chemoembolization and systemic therapy with sorafenib.
Keywords: SIR-spheres; TheraSphere; Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); Yttrium-90 (Y-90) microspheres; radioembolization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the survival and tolerability of radioembolization in elderly vs. younger patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2013 Oct;59(4):753-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.05.025. Epub 2013 May 23. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23707371 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment options for unresectable HCC with a focus on SIRT with Yttrium-90 resin microspheres.Int J Clin Pract. 2017 Nov;71(11). doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12972. Epub 2017 Jul 30. Int J Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 28758319 Review.
-
Transarterial Radioembolization Versus Atezolizumab-Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Matching-Adjusted Indirect Comparison of Time to Deterioration in Quality of Life.Adv Ther. 2022 May;39(5):2035-2051. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02099-0. Epub 2022 Mar 12. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35279814 Free PMC article.
-
For Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Yttrium-90 Microspheres, Dose Volumetrics on Post-Treatment Bremsstrahlung SPECT/CT Predict Clinical Outcomes.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 20;15(3):645. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030645. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36765603 Free PMC article.
-
Radioembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2010 Dec;7(4):247-52. doi: 10.2174/157016310793360701. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2010. PMID: 21034410 Review.
Cited by
-
Examining the Efficacy and Safety of Combined Locoregional Therapy and Immunotherapy in Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 27;12(7):1432. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071432. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung shunt fraction calculation using 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT imaging for 90Y microsphere selective internal radiation therapy of liver tumors.EJNMMI Res. 2021 Sep 28;11(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13550-021-00837-z. EJNMMI Res. 2021. PMID: 34585259 Free PMC article.
-
Yttrium-90 transarterial radioembolization for liver metastases from medullary thyroid cancer.Eur Thyroid J. 2022 Oct 17;11(6):e220130. doi: 10.1530/ETJ-22-0130. Print 2022 Dec 1. Eur Thyroid J. 2022. PMID: 36126186 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemic Cholangiopathy Following Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Hepatectomy: an Underestimated and Devastating Complication.J Gastrointest Surg. 2020 Nov;24(11):2517-2525. doi: 10.1007/s11605-019-04409-4. Epub 2019 Nov 21. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020. PMID: 31754989
-
Liver Resection After Selective Internal Radiation Therapy with Yttrium-90: Safety and Outcomes.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2020 Mar;51(1):152-158. doi: 10.1007/s12029-019-00221-0. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2020. PMID: 30911980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011;61:69-90. - PubMed
-
- A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients: the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. Hepatology 1998;28:751-5. - PubMed
-
- McDermott WV, Cady B, Georgi B, et al. Primary cancer of the liver. Evaluation, treatment, and prognosis. Arch Surg 1989;124:552-4; discussion 554-5. - PubMed
-
- Johnson PJ. Why can't we cure primary liver cancer? Eur J Cancer 1995;31A:1562-4. - PubMed
-
- Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L, et al. Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: long-term results of percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation. Radiology 2005;234:961-7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
