Recent advances in the treatment of melanoma with BRAF and MEK inhibitors
- PMID: 26488003
- PMCID: PMC4583602
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.05.13
Recent advances in the treatment of melanoma with BRAF and MEK inhibitors
Abstract
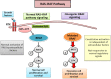
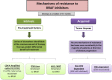
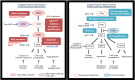
Selective inhibition of the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway with either BRAF or MEK inhibition has emerged as the key component for the treatment of BRAF-mutant metastatic melanoma. New evidence from several phase III trials suggests that the combination of BRAF and MEK inhibitors improves tumor response rate and progression-free survival (PFS). Some of the serious adverse events, in particular, the incidence of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma seen with the monotherapy treatment with a BRAF inhibitor are attenuated with combination therapy, whereas milder side effects such as pyrexia can be more common with combination therapy. Although dose reductions and dose interruptions are slightly more common with combination therapy, overall data supports the notion that combination therapy is safe and improves the outcomes for metastatic melanoma patients compared to single agent BRAF inhibitors.
Keywords: BRAF inhibitor; BRAF mutation; MEK inhibitor; Metastatic melanoma; NRAS mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Heideman DA, Lurkin I, Doeleman M, et al. KRAS and BRAF mutation analysis in routine molecular diagnostics: comparison of three testing methods on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor-derived DNA. J Mol Diagn 2012;14:247-55. - PubMed
-
- Devitt B, Liu W, Salemi R, et al. Clinical outcome and pathological features associated with NRAS mutation in cutaneous melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 2011;24:666-72. - PubMed
-
- Eskandarpour M, Huang F, Reeves KA, et al. Oncogenic NRAS has multiple effects on the malignant phenotype of human melanoma cells cultured in vitro. Int J Cancer 2009;124:16-26. - PubMed
-
- Eskandarpour M, Kiaii S, Zhu C, et al. Suppression of oncogenic NRAS by RNA interference induces apoptosis of human melanoma cells. Int J Cancer 2005;115:65-73. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous