How Is Fe-S Cluster Formation Regulated?
- PMID: 26488283
- PMCID: PMC7487215
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-micro-091014-104457
How Is Fe-S Cluster Formation Regulated?
Abstract
Iron-sulfur (Fe-S) clusters are fundamental to numerous biological processes in most organisms, but these protein cofactors can be prone to damage by various oxidants (e.g., O2, reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen species) and toxic levels of certain metals (e.g., cobalt and copper). Furthermore, their synthesis can also be directly influenced by the level of available iron in the environment. Consequently, the cellular need for Fe-S cluster biogenesis varies with fluctuating growth conditions. To accommodate changes in Fe-S demand, microorganisms employ diverse regulatory strategies to tailor Fe-S cluster biogenesis according to their surroundings. Here, we review the mechanisms that regulate Fe-S cluster formation in bacteria, primarily focusing on control of the Isc and Suf Fe-S cluster biogenesis systems in the model bacterium Escherichia coli.
Keywords: Fe-S; Isc pathway; Suf pathway; homeostasis; iron-sulfur cluster; regulation.
Figures
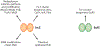

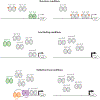
References
-
- Adinolfi S, Iannuzzi C, Prischi F, Pastore C, Iametti S, et al. 2009. Bacterial frataxin CyaY is the gatekeeper of iron-sulfur cluster formation catalyzed by IscS. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 16:390–96 - PubMed
-
- Angelini S, Gerez C, Ollagnier-de Choudens S, Sanakis Y, Fontecave M, et al. 2008. NfuA, a new factor required for maturing Fe/S proteins in Escherichia coli under oxidative stress and iron starvation conditions. J. Biol. Chem 283:14084–91 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

