Exosome-mediated microRNA transfer plays a role in radiation-induced bystander effect
- PMID: 26488306
- PMCID: PMC4829325
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1100795
Exosome-mediated microRNA transfer plays a role in radiation-induced bystander effect
Abstract
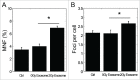
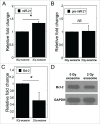
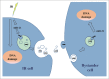
Bystander effects can be induced through cellular communication between irradiated cells and non-irradiated cells. The signals that mediate this cellular communication, such as cytokines, reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide and even microRNAs, can be transferred between cells via gap junctions or extracellular medium. We have previously reported that miR-21, a well described DDR (DNA damage response) microRNA, is involved in radiation-induced bystander effects through a medium-mediated way. However, the mechanisms of the microRNA transfer have not been elucidated in details. In the present study, it was found that exosomes isolated from irradiated conditioned medium could induce bystander effects. Furthermore, we demonstrated plenty of evidences that miR-21, which is up-regulated as a result of mimic transfection or irradiation, can be transferred from donor or irradiated cells into extracellular medium and subsequently get access to the recipient or bystander cells through exosomes to induce bystander effects. Inhibiting the miR-21 expression in advance can offset the bystander effects to some extent. From all of these results, it can be concluded that the exosome-mediated microRNA transfer plays an important role in the radiation-induced bystander effects. These findings provide new insights into the functions of microRNAs and the cellular communication between the directly irradiated cells and the non-irradiated cells.
Keywords: bystander effect; exosome; miR-21; microRNA; radiation.
Figures



References
-
- Banaz-Yasar F, Lennartz K, Winterhager E, Gellhaus A. Radiation-induced bystander effects in malignant trophoblast cells are independent from gap junctional communication. J Cell Biochem 2008; 103:149-61; PMID:17516549 - PubMed
-
- Ryan LA, Smith RW, Seymour CB, Mothersill CE. Dilution of irradiated cell conditioned medium and the bystander effect. Radiation Res 2008; 169:188-96; PMID:18220470 - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Yu KN, Hou J, Liu Q, Han W. Radiation-induced bystander effect: Early process and rapid assessment. Cancer Lett 2013; 356(1):137-44; PMID:24139967 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
