Structures of multidrug and toxic compound extrusion transporters and their mechanistic implications
- PMID: 26488689
- PMCID: PMC4960993
- DOI: 10.1080/19336950.2015.1106654
Structures of multidrug and toxic compound extrusion transporters and their mechanistic implications
Abstract
Multidrug resistance poses grand challenges to the effective treatment of infectious diseases and cancers. Integral membrane proteins from the multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) family contribute to multidrug resistance by exporting a wide variety of therapeutic drugs across cell membranes. MATE proteins are conserved from bacteria to humans and can be categorized into the NorM, DinF and eukaryotic subfamilies. MATE transporters hold great appeal as potential therapeutic targets for curbing multidrug resistance, yet their transport mechanism remains elusive. During the past 5 years, X-ray structures of 4 NorM and DinF transporters have been reported and guided biochemical studies to reveal how MATE transporters extrude different drugs. Such advances, although substantial, have yet to be discussed collectively. Herein I review these structures and the unprecedented mechanistic insights that have been garnered from those structure-inspired studies, as well as lay out the outstanding questions that present exciting opportunities for future work.
Keywords: cation binding; membrane transporter; multidrug efflux inhibitor; multidrug resistance; substrate recognition.
Figures

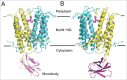
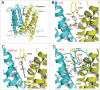
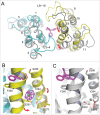

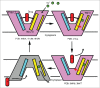
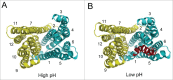
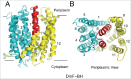
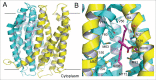

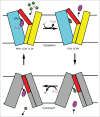

References
-
- Higgins CF. Multiple molecular mechanisms for multidrug resistance transporters. Nature 2007; 446:749-57; PMID:17429392; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nature05630 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fischbach MA, Walsh CT. Antibiotics for emerging pathogens. Science 2009; 325:1089-93; PMID:19713519; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1126/science.1176667 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown MH, Paulsen IT, Skurray RA. The multidrug efflux protein NorM is a prototype of a new family of transporters. Mol Microbiol 1999; 31:394-5; PMID:9987140; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01162.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Omote H, Miasa M, Matsumoto T, Otsuka M, Moroyama Y. The MATE proteins as fundamental transporters of metabolic and xenobiotic organic cations. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2006; 27:587-93; PMID:16996621; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.tips.2006.09.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuroda T, Tsuchiya T. Multidrug efflux transporters in the MATE family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009; 1794:763-8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
