Natural Killer Cell Memory
- PMID: 26488815
- PMCID: PMC4621966
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.09.013
Natural Killer Cell Memory
Abstract
Natural killer (NK) cells have historically been considered short-lived cytolytic cells that can rapidly respond against pathogens and tumors in an antigen-independent manner and then undergo cell death. Recently, however, NK cells have been shown to possess traits of adaptive immunity and can acquire immunological memory in a manner similar to that of T and B cells. In this review, we discuss evidence of NK cell memory and the mechanisms involved in the generation and survival of these innate lymphocytes.
Keywords: cytomegalovirus; immunological memory; natural killer cells.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

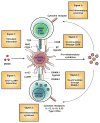
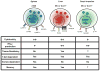

References
-
- Arase H, Mocarski ES, Campbell AE, Hill AB, Lanier LL. Direct recognition of cytomegalovirus by activating and inhibitory NK cell receptors. Science. 2002;296:1323–1326. - PubMed
-
- Artis D, Spits H. The biology of innate lymphoid cells. Nature. 2015;517:293–301. - PubMed
-
- Beziat V, Dalgard O, Asselah T, Halfon P, Bedossa P, Boudifa A, Hervier B, Theodorou I, Martinot M, Debre P, et al. CMV drives clonal expansion of NKG2C+ NK cells expressing self-specific KIRs in chronic hepatitis patients. European journal of immunology. 2012;42:447–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

