The Pathological Buying Screener: Development and Psychometric Properties of a New Screening Instrument for the Assessment of Pathological Buying Symptoms
- PMID: 26488872
- PMCID: PMC4619303
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141094
The Pathological Buying Screener: Development and Psychometric Properties of a New Screening Instrument for the Assessment of Pathological Buying Symptoms
Abstract
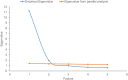
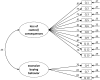
The study was designed to develop a new screening instrument for pathological buying (PB), and to examine its psychometric properties in a large-scale sample. By using a facet theoretical approach and based on literature as well as on clinical experience, a 20-item Pathological Buying Screener (PBS) was developed and administered to a representative German sample (n = 2,539). Valid data were available from 2,403 participants who were subjects for three subsequent empirical studies. The first study explored the factor structure using exploratory factor analyses in a subsample of 498 participants. Based on factor loadings, a 13-item version with the two factors loss of control / consequences and excessive buying behavior was revealed. This two-factor model was confirmed in study 2 by confirmatory factor analysis performed on another subsample (n = 1,905). Study 3 investigated age and gender effects and convergent validity of the PBS using the Compulsive Buying Scale (CBS) in the full sample (N = 2,403). The total PBS score was adequately correlated with the CBS score. Hierarchical regression analyses with the CBS score as the dependent variable and the two PBS factors as the predictors indicated an own incremental validity of the two factors in participants ≤ 65 years. The reliability of the total score as well as of the two subscales was good to excellent. Overall, the PBS represents a useful measure for PB. Future studies are needed to replicate the two-factor structure in clinical samples and to define a valid cutoff for PB.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The Pathological Buying Screener: Validation in a Clinical Sample].Psychother Psychosom Med Psychol. 2021 Jul;71(7):294-300. doi: 10.1055/a-1303-4743. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Psychother Psychosom Med Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33246347 German.
-
Spanish validation of the pathological buying screener in patients with eating disorder and gambling disorder.J Behav Addict. 2019 Mar 1;8(1):123-134. doi: 10.1556/2006.8.2019.08. J Behav Addict. 2019. PMID: 30932708 Free PMC article.
-
Estimated prevalence of compulsive buying in Germany and its association with sociodemographic characteristics and depressive symptoms.Psychiatry Res. 2010 Dec 30;180(2-3):137-42. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2009.12.001. Epub 2010 May 21. Psychiatry Res. 2010. PMID: 20494451
-
Measuring compulsive buying behaviour: psychometric validity of three different scales and prevalence in the general population and in shopping centres.Psychiatry Res. 2015 Feb 28;225(3):326-34. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2014.11.080. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Psychiatry Res. 2015. PMID: 25595336
-
The prevalence of compulsive buying: a meta-analysis.Addiction. 2016 Mar;111(3):408-19. doi: 10.1111/add.13223. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Addiction. 2016. PMID: 26517309 Review.
Cited by
-
Online compulsive buying behavior and its association with internet addiction, self-esteem, impulsiveness, and emotional distress among nursing students.Ind Psychiatry J. 2024 Jul-Dec;33(2):253-259. doi: 10.4103/ipj.ipj_351_24. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Ind Psychiatry J. 2024. PMID: 39898089 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Food Addiction Across Several Behavioral Addictions: Analysis of Clinical Relevance.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 6;17(7):1279. doi: 10.3390/nu17071279. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40219036 Free PMC article.
-
A Study to Assess the Prevalence and Determinants of Compulsive Buying Disorder Among College Students in Chengalpattu District, Tamil Nadu.Cureus. 2025 Jun 9;17(6):e85664. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85664. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40642701 Free PMC article.
-
Is online shopping addiction still a depressive illness? -- the induced consumption and traffic trap in live E-commerce.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 21;10(9):e29895. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29895. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38694126 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship of Shopping-Related Decisions with Materialistic Values Endorsement, Compulsive Buying-Shopping Disorder Symptoms and Everyday Moral Decision Making.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 5;19(7):4376. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19074376. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35410054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kraepelin E. Psychiatrie Ein Lehrbuch für Studierende und Ärzte. Leipzig: Johann Ambrosius Barth; 1909. pp. 408–409.
-
- Koran L, Faber R, Aboujaoude E, Large M, Serpe R. Estimated prevalence of compulsive buying behavior in the United States. Am J Psychiatry. 2006; 163: 1806–1812. - PubMed
-
- Neuner M, Raab G, Reisch L. Compulsive buying in maturing consumer societies: an empirical re-inquiry. J Econ Psychol. 2005; 26: 509–522.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources