Identification of Non-nucleoside Human Ribonucleotide Reductase Modulators
- PMID: 26488902
- PMCID: PMC4751996
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00929
Identification of Non-nucleoside Human Ribonucleotide Reductase Modulators
Abstract
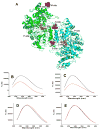
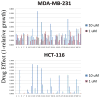
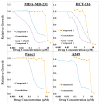
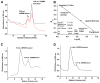
Ribonucleotide reductase (RR) catalyzes the rate-limiting step of dNTP synthesis and is an established cancer target. Drugs targeting RR are mainly nucleoside in nature. In this study, we sought to identify non-nucleoside small-molecule inhibitors of RR. Using virtual screening, binding affinity, inhibition, and cell toxicity, we have discovered a class of small molecules that alter the equilibrium of inactive hexamers of RR, leading to its inhibition. Several unique chemical categories, including a phthalimide derivative, show micromolar IC50s and KDs while demonstrating cytotoxicity. A crystal structure of an active phthalimide binding at the targeted interface supports the noncompetitive mode of inhibition determined by kinetic studies. Furthermore, the phthalimide shifts the equilibrium from dimer to hexamer. Together, these data identify several novel non-nucleoside inhibitors of human RR which act by stabilizing the inactive form of the enzyme.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jordheim LP, Seve P, Tredan O, Dumontet C. The ribonucleotide reductase large subunit (RRM1) as a predictive factor in patients with cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:693–702. - PubMed
-
- Jordheim LP, Guittet O, Lepoivre M, Galmarini CM, Dumontet C. Increased expression of the large subunit of ribonucleotide reductase is involved in resistance to gemcitabine in human mammary adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:1268–1276. - PubMed
-
- Shao J, Zhou B, Chu B, Yen Y. Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors and future drug design. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2006;6:409–431. - PubMed
-
- Huang P, Chubb S, Plunkett W. Termination of DNA synthesis by 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine. A mechanism for cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:16617–16625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

