Renoprotective Mechanism of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Based on Transcriptomic Analysis in a Porcine Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Model
- PMID: 26489007
- PMCID: PMC4619554
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141099
Renoprotective Mechanism of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Based on Transcriptomic Analysis in a Porcine Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Model
Abstract
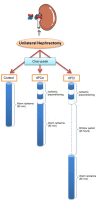
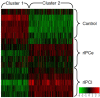
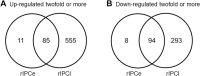
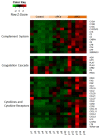
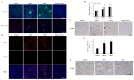
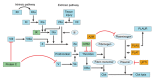
Ischemic preconditioning (IPC) is a well-known phenomenon in which tissues are exposed to a brief period of ischemia prior to a longer ischemic event. This technique produces tissue tolerance to ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI). Currently, IPC's mechanism of action is poorly understood. Using a porcine single kidney model, we performed remote IPC with renal IRI and evaluated the IPC mechanism of action. Following left nephrectomy, 15 female Yorkshire pigs were divided into three groups: no IPC and 90 minutes of warm ischemia (control), remote IPC immediately followed by 90 minutes of warm ischemia (rIPCe), and remote IPC with 90 minutes of warm ischemia performed 24 hours later (rIPCl). Differential gene expression analysis was performed using a porcine-specific microarray. The microarray analysis of porcine renal tissues identified 1,053 differentially expressed probes in preconditioned pigs. Among these, 179 genes had altered expression in both the rIPCe and rIPCl groups. The genes were largely related to oxidation reduction, apoptosis, and inflammatory response. In the rIPCl group, an additional 848 genes had altered expression levels. These genes were primarily related to immune response and inflammation, including those coding for cytokines and cytokine receptors and those that play roles in the complement system and coagulation cascade. In the complement system, the membrane attack complex was determined to be sublytic, because it colocalized with phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Furthermore, alpha 2 macroglobulin, tissue plasminogen activator, uterine plasmin trypsin inhibitor, and arginase-1 mRNA levels were elevated in the rIPCl group. These findings indicate that remote IPC produces renoprotective effects through multiple mechanisms, and these effects develop over a long timeframe rather than immediately following IPC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ischemia preconditioning does not confer resilience to warm ischemia in a solitary porcine kidney model.Urology. 2007 May;69(5):984-7. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2007.01.100. Urology. 2007. PMID: 17482956
-
Effects of ischemic preconditioning protocols on skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury.J Surg Res. 2015 Feb;193(2):942-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.09.032. Epub 2014 Sep 30. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25438960
-
Ischemic preconditioning improved renal ischemia/reperfusion injury and hyperglycemia.IUBMB Life. 2019 Mar;71(3):321-329. doi: 10.1002/iub.1972. Epub 2018 Nov 27. IUBMB Life. 2019. PMID: 30481400
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning: a novel protective method from ischemia reperfusion injury--a review.J Surg Res. 2008 Dec;150(2):304-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.12.747. Epub 2008 Jan 22. J Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 19040966 Review.
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning for kidney protection: GSK3β-centric insights into the mechanism of action.Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Nov;66(5):846-56. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.06.026. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 26271146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the effect of remote ischemic preconditioning on kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury.J Res Med Sci. 2020 Jan 20;25:6. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_249_19. eCollection 2020. J Res Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32055246 Free PMC article.
-
No Effect of Remote Ischemic Conditioning Strategies on Recovery from Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Protective Molecular Mediators.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 31;10(12):e0146109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146109. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26720280 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-α-induced Inflammation Stimulates Apolipoprotein-A4 via Activation of TNFR2 and NF-κB Signaling in Kidney Tubular Cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 18;7(1):8856. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08785-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28821873 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon monoxide-releasing molecule-3: Amelioration of renal ischemia reperfusion injury in a rat model.Investig Clin Urol. 2020 Jul;61(4):441-451. doi: 10.4111/icu.2020.61.4.441. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Investig Clin Urol. 2020. PMID: 32666002 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of the effect of remote ischaemic conditioning in an animal model of necrotising enterocolitis.Sci Rep. 2024 May 11;14(1):10783. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61482-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38734725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74:1124–36. - PubMed
-
- Serafin A, Fernandez-Zabalegui L, Prats N, Wu ZY, Rosello-Catafau J, Peralta C. Ischemic preconditioning: tolerance to hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Histology and histopathology. 2004;19:281–9. - PubMed
-
- Simon C, Vara E, Garutti I, Gonzalez-Casaurran G, Azcarate L, Isea J, et al. Modulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression by ischaemic preconditioning in a lung autotransplant model. European journal of cardio-thoracic surgery: official journal of the European Association for Cardio-thoracic Surgery. 2012;41:933–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

