Raloxifene improves skeletal properties in an animal model of cystic chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 26489025
- PMCID: PMC4840093
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2015.315
Raloxifene improves skeletal properties in an animal model of cystic chronic kidney disease
Abstract
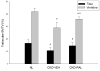
Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have an increased risk of fracture. Raloxifene is a mild antiresorptive agent that reduces fracture risk in the general population. Here we assessed the impact of raloxifene on the skeletal properties of animals with progressive CKD. Male Cy/+ rats that develop autosomal dominant cystic kidney disease were treated with either vehicle or raloxifene for five weeks. They were assessed for changes in mineral metabolism and skeletal parameters (microCT, histology, whole-bone mechanics, and material properties). Their normal littermates served as controls. Animals with CKD had significantly higher parathyroid hormone levels compared with normal controls, as well as inferior structural and mechanical skeletal properties. Raloxifene treatment resulted in lower bone remodeling rates and higher cancellous bone volume in the rats with CKD. Although it had little effect on cortical bone geometry, it resulted in higher energy to fracture and modulus of toughness values than vehicle-treated rats with CKD, achieving levels equivalent to normal controls. Animals treated with raloxifene had superior tissue-level mechanical properties as assessed by nanoindentation, and higher collagen D-periodic spacing as assessed by atomic force microscopy. Thus, raloxifene can positively impact whole-bone mechanical properties in CKD through its impact on skeletal material properties.
Keywords: bone quality; chronic kidney disease; raloxifene.
Copyright © 2015 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to the described work.
Figures



Comment in
-
Bone strength: more than just bone density.Kidney Int. 2016 Jan;89(1):16-9. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2015.11.004. Kidney Int. 2016. PMID: 26759040
References
-
- Levey AS, Eckardt KU, Tsukamoto Y, Levin A, Coresh J, Rossert J, Zeeuw D, Hostetter TH, Lameire N, Eknoyan G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Kidney Int. 2005;67:2089–2100. - PubMed
-
- Levin A, Bakris GL, Molitch M, Smulders M, Tian J, Williams LA, Andress DL. Prevalence of abnormal serum vitamin D, PTH, calcium, and phosphorus in patients with chronic kidney disease: results of the study to evaluate early kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2007;71:31–38. - PubMed
-
- KDIGO . Clinical practice guidelines for the management of CKD–MBD. Kidney Int. 2009;76:S1–S130. - PubMed
-
- Ott SM. Therapy for patients with CKD and low bone mineral density. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013;9:681–692. - PubMed
-
- McClung M, et al. Bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis: benefits, risks, and drug holiday. Am J Med. 2013;126:13–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

