Handling of Drugs, Metabolites, and Uremic Toxins by Kidney Proximal Tubule Drug Transporters
- PMID: 26490509
- PMCID: PMC4633783
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.02440314
Handling of Drugs, Metabolites, and Uremic Toxins by Kidney Proximal Tubule Drug Transporters
Abstract
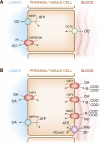
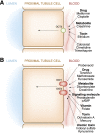
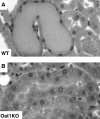
The proximal tubule of the kidney plays a crucial role in the renal handling of drugs (e.g., diuretics), uremic toxins (e.g., indoxyl sulfate), environmental toxins (e.g., mercury, aristolochic acid), metabolites (e.g., uric acid), dietary compounds, and signaling molecules. This process is dependent on many multispecific transporters of the solute carrier (SLC) superfamily, including organic anion transporter (OAT) and organic cation transporter (OCT) subfamilies, and the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) superfamily. We review the basic physiology of these SLC and ABC transporters, many of which are often called drug transporters. With an emphasis on OAT1 (SLC22A6), the closely related OAT3 (SLC22A8), and OCT2 (SLC22A2), we explore the implications of recent in vitro, in vivo, and clinical data pertinent to the kidney. The analysis of murine knockouts has revealed a key role for these transporters in the renal handling not only of drugs and toxins but also of gut microbiome products, as well as liver-derived phase 1 and phase 2 metabolites, including putative uremic toxins (among other molecules of metabolic and clinical importance). Functional activity of these transporters (and polymorphisms affecting it) plays a key role in drug handling and nephrotoxicity. These transporters may also play a role in remote sensing and signaling, as part of a versatile small molecule communication network operative throughout the body in normal and diseased states, such as AKI and CKD.
Keywords: ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters; Acute Kidney Injury; Anti-Bacterial Agents; Cations; Chronic; Diuretics; Organic Anion Transporters; Renal Insufficiency; drug transporter; nephrotoxicity; renal physiology.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Burckhardt G: Drug transport by Organic Anion Transporters (OATs). Pharmacol Ther 136: 106–130, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Nigam SK, Bhatnagar V: How much do we know about drug handling by SLC and ABC drug transporters in children? Clin Pharmacol Ther 94: 27–29, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Nigam SK, Bush KT, Bhatnagar V: Drug and toxicant handling by the OAT organic anion transporters in the kidney and other tissues. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 3: 443–448, 2007 - PubMed
-
- VanWert AL, Gionfriddo MR, Sweet DH: Organic anion transporters: Discovery, pharmacology, regulation and roles in pathophysiology. Biopharm Drug Dispos 31: 1–71, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

