Methods for biological data integration: perspectives and challenges
- PMID: 26490630
- PMCID: PMC4685837
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2015.0571
Methods for biological data integration: perspectives and challenges
Abstract
Rapid technological advances have led to the production of different types of biological data and enabled construction of complex networks with various types of interactions between diverse biological entities. Standard network data analysis methods were shown to be limited in dealing with such heterogeneous networked data and consequently, new methods for integrative data analyses have been proposed. The integrative methods can collectively mine multiple types of biological data and produce more holistic, systems-level biological insights. We survey recent methods for collective mining (integration) of various types of networked biological data. We compare different state-of-the-art methods for data integration and highlight their advantages and disadvantages in addressing important biological problems. We identify the important computational challenges of these methods and provide a general guideline for which methods are suited for specific biological problems, or specific data types. Moreover, we propose that recent non-negative matrix factorization-based approaches may become the integration methodology of choice, as they are well suited and accurate in dealing with heterogeneous data and have many opportunities for further development.
Keywords: biological networks; data fusion; heterogeneous data integration; non-negative matrix factorization; omics data; systems biology.
© 2015 The Author(s).
Figures
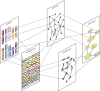
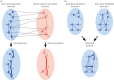
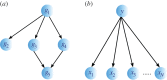
 . (b) An example of a naive BN with a class node y being the parent to independent nodes x1, x2 , … , xN.
. (b) An example of a naive BN with a class node y being the parent to independent nodes x1, x2 , … , xN.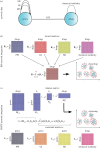
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

