Generation and analysis of knock-in mice carrying pseudohypoaldosteronism type II-causing mutations in the cullin 3 gene
- PMID: 26490675
- PMCID: PMC4728349
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.013276
Generation and analysis of knock-in mice carrying pseudohypoaldosteronism type II-causing mutations in the cullin 3 gene
Abstract
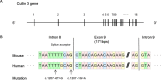
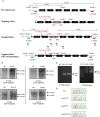
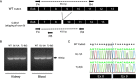
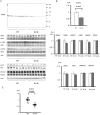
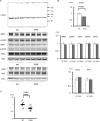
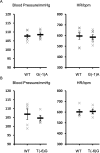
Pseudohypoaldosteronism type II (PHAII) is a hereditary hypertensive disease caused by mutations in four different genes: with-no-lysine kinases (WNK) 1 and 4, Kelch-like family member 3 (KLHL3), and cullin 3 (Cul3). Cul3 and KLHL3 form an E3 ligase complex that ubiquitinates and reduces the expression level of WNK4. PHAII-causing mutations in WNK4 and KLHL3 impair WNK4 ubiquitination. However, the molecular pathogenesis of PHAII caused by Cul3 mutations is unclear. In cultured cells and human leukocytes, PHAII-causing Cul3 mutations result in the skipping of exon 9, producing mutant Cul3 protein lacking 57 amino acids. However, whether this phenomenon occurs in the kidneys and is responsible for the pathogenesis of PHAII in vivo is unknown. We generated knock-in mice carrying a mutation in the C-terminus of intron 8 of Cul3, c.1207-1G>A, which corresponds to a PHAII-causing mutation in the human Cul3 gene. Heterozygous Cul3(G(-1)A/+) knock-in mice did not exhibit PHAII phenotypes, and the skipping of exon 9 was not evident in their kidneys. However, the level of Cul3 mRNA expression in the kidneys of heterozygous knock-in mice was approximately half that of wild-type mice. Furthermore, homozygous knock-in mice were nonviable. It suggested that the mutant allele behaved like a knockout allele and did not produce Cul3 mRNA lacking exon 9. A reduction in Cul3 expression alone was not sufficient to develop PHAII in the knock-in mice. Our findings highlighted the pathogenic role of mutant Cul3 protein and provided insight to explain why PHAII-causing mutations in Cul3 cause kidney-predominant PHAII phenotypes.
Keywords: Cullin 3; Hypertension; PHAII.
© 2015. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decreased KLHL3 expression is involved in the pathogenesis of pseudohypoaldosteronism type II caused by cullin 3 mutation in vivo.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2018 Dec;22(6):1251-1257. doi: 10.1007/s10157-018-1593-z. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29869755
-
Impaired degradation of WNK1 and WNK4 kinases causes PHAII in mutant KLHL3 knock-in mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Oct 1;23(19):5052-60. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu217. Epub 2014 May 12. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24821705
-
Generation and analysis of a mouse model of pseudohypoaldosteronism type II caused by KLHL3 mutation in BTB domain.FASEB J. 2019 Jan;33(1):1051-1061. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801023R. Epub 2018 Aug 27. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30148674
-
Kelch-like 3/Cullin 3 ubiquitin ligase complex and WNK signaling in salt-sensitive hypertension and electrolyte disorder.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016 Sep;31(9):1417-24. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv259. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26152401 Review.
-
Regulation of blood pressure and renal electrolyte balance by Cullin-RING ligases.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2014 Sep;23(5):487-93. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000049. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 24992566 Review.
Cited by
-
Familial Hyperkalemic Hypertension.Compr Physiol. 2024 Dec 19;14(5):5839-5874. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c240004. Compr Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39699086 Review.
-
Mutant Cullin 3 causes familial hyperkalemic hypertension via dominant effects.JCI Insight. 2017 Dec 21;2(24):e96700. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.96700. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 29263298 Free PMC article.
-
ROMK expression remains unaltered in a mouse model of familial hyperkalemic hypertension caused by the CUL3Δ403-459 mutation.Physiol Rep. 2016 Jul;4(13):e12850. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12850. Physiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27378813 Free PMC article.
-
The WNK signaling pathway and salt-sensitive hypertension.Hypertens Res. 2020 Aug;43(8):733-743. doi: 10.1038/s41440-020-0437-x. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Hypertens Res. 2020. PMID: 32286498 Review.
-
Insights into the diverse mechanisms and effects of variant CUL3-induced familial hyperkalemic hypertension.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Oct 16;21(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01269-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37845702 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chiga M., Rafiqi F. H., Alessi D. R., Sohara E., Ohta A., Rai T., Sasaki S. and Uchida S. (2011). Phenotypes of pseudohypoaldosteronism type II caused by the WNK4 D561A missense mutation are dependent on the WNK-OSR1/SPAK kinase cascade. J. Cell Sci. 124, 1391-1395. 10.1242/jcs.084111 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

