Structural basis for suppression of hypernegative DNA supercoiling by E. coli topoisomerase I
- PMID: 26490962
- PMCID: PMC4678816
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv1073
Structural basis for suppression of hypernegative DNA supercoiling by E. coli topoisomerase I
Abstract
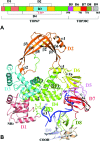
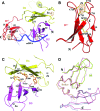
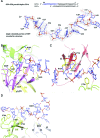
Escherichia coli topoisomerase I has an essential function in preventing hypernegative supercoiling of DNA. A full length structure of E. coli topoisomerase I reported here shows how the C-terminal domains bind single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) to recognize the accumulation of negative supercoils in duplex DNA. These C-terminal domains of E. coli topoisomerase I are known to interact with RNA polymerase, and two flexible linkers within the C-terminal domains may assist in the movement of the ssDNA for the rapid removal of transcription driven negative supercoils. The structure has also unveiled for the first time how the 4-Cys zinc ribbon domain and zinc ribbon-like domain bind ssDNA with primarily π-stacking interactions. This novel structure, in combination with new biochemical data, provides important insights into the mechanism of genome regulation by type IA topoisomerases that is essential for life, as well as the structures of homologous type IA TOP3α and TOP3β from higher eukaryotes that also have multiple 4-Cys zinc ribbon domains required for their physiological functions.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Direct interaction between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and the zinc ribbon domains of DNA topoisomerase I.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 15;278(33):30705-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303403200. Epub 2003 Jun 4. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12788950
-
The role of the Zn(II) binding domain in the mechanism of E. coli DNA topoisomerase I.BMC Biochem. 2002 May 29;3:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2091-3-13. BMC Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12052259 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Susceptibility and SOS-Dependent Increase in Mutation Frequency Are Impacted by Escherichia coli Topoisomerase I C-Terminal Point Mutation.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Oct;59(10):6195-202. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00855-15. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26248366 Free PMC article.
-
[DNA supercoiling and topoisomerases in Escherichia coli].Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1995 Jul-Sep;37(3):291-304. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8850348 Review. Spanish.
-
Structure and mechanism of DNA topoisomerases.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1995;24:185-208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.24.060195.001153. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1995. PMID: 7663114 Review.
Cited by
-
Model of abasic site DNA cross-link repair; from the architecture of NEIL3 DNA binding domains to the X-structure model.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Oct 14;50(18):10436-10448. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac793. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36155818 Free PMC article.
-
Probing hyper-negatively supercoiled mini-circles with nucleases and DNA binding proteins.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 16;13(8):e0202138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202138. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30114256 Free PMC article.
-
Topoisomerases I and III inhibit R-loop formation to prevent unregulated replication in the chromosomal Ter region of Escherichia coli.PLoS Genet. 2018 Sep 17;14(9):e1007668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007668. eCollection 2018 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30222737 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological variants in TOP3A cause distinct disorders of mitochondrial and nuclear genome stability.EMBO Mol Med. 2023 May 8;15(5):e16775. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202216775. Epub 2023 Apr 4. EMBO Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37013609 Free PMC article.
-
A highly processive actinobacterial topoisomerase I - thoughts on Streptomyces' demand for an enzyme with a unique C-terminal domain.Microbiology (Reading). 2020 Feb;166(2):120-128. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000841. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Microbiology (Reading). 2020. PMID: 31390324 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen S.H., Chan N.L., Hsieh T.S. New mechanistic and functional insights into DNA topoisomerases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013;82:139–170. - PubMed
-
- Drolet M. Growth inhibition mediated by excess negative supercoiling: The interplay between transcription elongation, R-loop formation and DNA topology. Mol. Microbiol. 2006;59:723–730. - PubMed
-
- Drolet M., Broccoli S., Rallu F., Hraiky C., Fortin C., Masse E., Baaklini I. The problem of hypernegative supercoiling and R-loop formation in transcription. Front. Biosci. 2003;8:d210–d221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

