α/β Hydrolase Domain-containing 6 (ABHD6) Degrades the Late Endosomal/Lysosomal Lipid Bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate
- PMID: 26491015
- PMCID: PMC4705992
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.669168
α/β Hydrolase Domain-containing 6 (ABHD6) Degrades the Late Endosomal/Lysosomal Lipid Bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate
Abstract
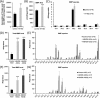
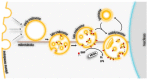
α/β Hydrolase domain-containing 6 (ABHD6) can act as monoacylglycerol hydrolase and is believed to play a role in endocannabinoid signaling as well as in the pathogenesis of obesity and liver steatosis. However, the mechanistic link between gene function and disease is incompletely understood. Here we aimed to further characterize the role of ABHD6 in lipid metabolism. We show that mouse and human ABHD6 degrade bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate (BMP) with high specific activity. BMP, also known as lysobisphosphatidic acid, is enriched in late endosomes/lysosomes, where it plays a key role in the formation of intraluminal vesicles and in lipid sorting. Up to now, little has been known about the catabolism of this lipid. Our data demonstrate that ABHD6 is responsible for ∼ 90% of the BMP hydrolase activity detected in the liver and that knockdown of ABHD6 increases hepatic BMP levels. Tissue fractionation and live-cell imaging experiments revealed that ABHD6 co-localizes with late endosomes/lysosomes. The enzyme is active at cytosolic pH and lacks acid hydrolase activity, implying that it degrades BMP exported from acidic organelles or de novo-formed BMP. In conclusion, our data suggest that ABHD6 controls BMP catabolism and is therefore part of the late endosomal/lysosomal lipid-sorting machinery.
Keywords: bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate; endocannabinoid; endosome; lipid metabolism; lysobisphosphatidic acid; lysosome; phospholipase.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Metabolic disease and ABHD6 alter the circulating bis(monoacylglycerol)phosphate profile in mice and humans.J Lipid Res. 2019 May;60(5):1020-1031. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M093351. Epub 2019 Mar 20. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 30894461 Free PMC article.
-
Bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate, a new lipid signature of endosome-derived extracellular vesicles.Biochimie. 2020 Nov;178:26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Biochimie. 2020. PMID: 32659447
-
Metabolic regulation of the lysosomal cofactor bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate in mice.J Lipid Res. 2020 Jul;61(7):995-1003. doi: 10.1194/jlr.RA119000516. Epub 2020 Apr 29. J Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 32350080 Free PMC article.
-
Biological function of the cellular lipid BMP-BMP as a key activator for cholesterol sorting and membrane digestion.Neurochem Res. 2011 Sep;36(9):1594-600. doi: 10.1007/s11064-010-0337-6. Epub 2010 Dec 7. Neurochem Res. 2011. PMID: 21136156 Review.
-
Bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate, an important actor in the host endocytic machinery hijacked by SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses.Biochimie. 2020 Dec;179:247-256. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2020.10.018. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Biochimie. 2020. PMID: 33159981 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipolysis: cellular mechanisms for lipid mobilization from fat stores.Nat Metab. 2021 Nov;3(11):1445-1465. doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00493-6. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Nat Metab. 2021. PMID: 34799702 Review.
-
To be or not to be a fat burner, that is the question for cpt1c in cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Jan 24;14(1):57. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05599-1. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36693836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Classical to Alternative Pathways of 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Synthesis: AlterAGs at the Crossroad of Endocannabinoid and Lysophospholipid Signaling.Molecules. 2024 Aug 4;29(15):3694. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153694. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39125098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Lipid Profiles after Dietary Intake of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Using Integrated Untargeted and Targeted Lipidomics.Metabolites. 2019 Oct 21;9(10):241. doi: 10.3390/metabo9100241. Metabolites. 2019. PMID: 31640217 Free PMC article.
-
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1C negatively regulates the endocannabinoid hydrolase ABHD6 in mice, depending on nutritional status.Br J Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;178(7):1507-1523. doi: 10.1111/bph.15377. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33444462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li F., Fei X., Xu J., and Ji C. (2009) An unannotated α/β hydrolase superfamily member, ABHD6 differentially expressed among cancer cell lines. Mol. Biol. Rep. 36, 691–696 - PubMed
-
- Marrs W. R., Blankman J. L., Horne E. A., Thomazeau A., Lin Y. H., Coy J., Bodor A. L., Muccioli G. G., Hu S. S., Woodruff G., Fung S., Lafourcade M., Alexander J. P., Long J. Z., Li W., Xu C., Möller T., Mackie K., Manzoni O. J., Cravatt B. F., and Stella N. (2010) The serine hydrolase ABHD6 controls the accumulation and efficacy of 2-AG at cannabinoid receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 951–957 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

