High Incidence of Invasive Group A Streptococcus Disease Caused by Strains of Uncommon emm Types in Thunder Bay, Ontario, Canada
- PMID: 26491184
- PMCID: PMC4702752
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02201-15
High Incidence of Invasive Group A Streptococcus Disease Caused by Strains of Uncommon emm Types in Thunder Bay, Ontario, Canada
Abstract
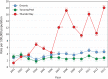
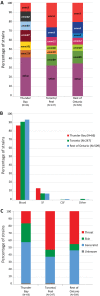
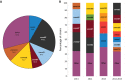
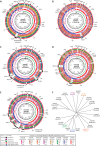
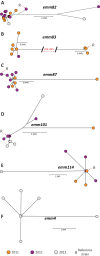
An outbreak of type emm59 invasive group A Streptococcus (iGAS) disease was declared in 2008 in Thunder Bay District, Northwestern Ontario, 2 years after a countrywide emm59 epidemic was recognized in Canada. Despite a declining number of emm59 infections since 2010, numerous cases of iGAS disease continue to be reported in the area. We collected clinical information on all iGAS cases recorded in Thunder Bay District from 2008 to 2013. We also emm typed and sequenced the genomes of all available strains isolated from 2011 to 2013 from iGAS infections and from severe cases of soft tissue infections. We used whole-genome sequencing data to investigate the population structure of GAS strains of the most frequently isolated emm types. We report an increased incidence of iGAS in Thunder Bay compared to the metropolitan area of Toronto/Peel and the province of Ontario. Illicit drug use, alcohol abuse, homelessness, and hepatitis C infection were underlying diseases or conditions that might have predisposed patients to iGAS disease. Most cases were caused by clonal strains of skin or generalist emm types (i.e., emm82, emm87, emm101, emm4, emm83, and emm114) uncommonly seen in other areas of the province. We observed rapid waxing and waning of emm types causing disease and their replacement by other emm types associated with the same tissue tropisms. Thus, iGAS disease in Thunder Bay District predominantly affects a select population of disadvantaged persons and is caused by clonally related strains of a few skin and generalist emm types less commonly associated with iGAS in other areas of Ontario.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Manjula BN, Acharya AS, Fairwell T, Fischetti VA. 1986. Antigenic domains of the streptococcal Pep M5 protein: localization of epitopes crossreactive with type 6 M protein and identification of a hypervariable region of the M molecule. J Exp Med 163:129–138. doi:10.1084/jem.163.1.129. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

