Development of polymer-bound fast-dissolving metformin buccal film with disintegrants
- PMID: 26491321
- PMCID: PMC4599618
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S80052
Development of polymer-bound fast-dissolving metformin buccal film with disintegrants
Abstract
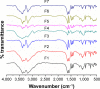
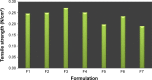
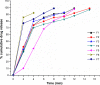
Fast-dissolving drug-delivery systems are considered advantageous over the existing conventional oral dosage forms like tablets, capsules, and syrups for being patient friendly. Buccal films are one such system responsible for systemic drug delivery at the desired site of action by avoiding hepatic first-pass metabolism. Metformin hydrochloride (Met), an antidiabetic drug, has poor bioavailability due to its high solubility and low permeability. The purpose of the study reported here was to develop a polymer-bound fast-dissolving buccal film of metformin to exploit these unique properties. In the study, metformin fast-dissolving films were prepared by the solvent-casting method using chitosan, a bioadhesive polymer. Further, starch, sodium starch glycolate, and microcrystalline cellulose were the disintegrants added to different ratios, forming various formulations (F1 to F7). The buccal films were evaluated for various parameters like weight variation, thickness, folding endurance, surface pH, content uniformity, tensile strength, and percentage of elongation. The films were also subjected to in vitro dissolution study, and the disintegration time was found to be less than 30 minutes for all formulations, which was attributed to the effect of disintegrants. Formulation F6 showed 92.2% drug release within 6 minutes due to the combined effect of sodium starch glycolate and microcrystalline cellulose.
Keywords: chitosan; drug-delivery system; immediate release; microcrystalline cellulose; sodium starch glycolate.
Figures
References
-
- Barnhart S, Vondrak B. Dissolvable films: dissolvable films for flex product format in drug delivery. Pharmtech.com [serial online] 2008. Apr 1, [Accessed March 17, 2015]. [about 5 p]. http://www.pharmtech.com/dissolvable-films-dissolvable-films-flexible-pr...
-
- Anders R, Merkle HP. Evaluation of laminated mucoadhesive patches for buccal drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 1989;49(3):231–240.
-
- Chen WG, Hwang GC. Adhesive and in vitro release characteristics of propranolol bioadhesive disc system. Int J Pharm. 1992;82(1–2):61–66.
-
- Alur HH, Pather SI, Mitra AK, Johnston TP. Transmucosal sustained-delivery of chlorpheniramine maleate in rabbits using a novel, natural mucoadhesive gum as an excipient in buccal tablets. Int J Pharm. 1999;188(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Guo JH. Bioadhesive polymer buccal patches for buprenorphine controlled delivery formulation in vitro adhesion and release properties. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1994;20(18):2809–2821.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous