Wear studies on plasma-sprayed Al2O3 and 8mole% of Yttrium-stabilized ZrO2 composite coating on biomedical Ti-6Al-4V alloy for orthopedic joint application
- PMID: 26491323
- PMCID: PMC4599621
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S79997
Wear studies on plasma-sprayed Al2O3 and 8mole% of Yttrium-stabilized ZrO2 composite coating on biomedical Ti-6Al-4V alloy for orthopedic joint application
Abstract
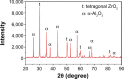
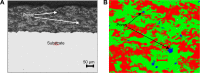
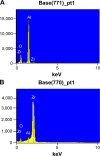
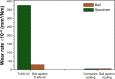
This paper presents the wear characteristics of the composite ceramic coating made with Al2O3-40wt%8YSZ on the biomedical grade Ti-6Al-4V alloy (grade 5) used for total joint prosthetic components, with the aim of improving their tribological behavior. The coatings were deposited using a plasma spraying technique, and optimization of plasma parameters was performed using response surface methodology to obtain dense coating. The tribological behaviors of the coated and uncoated substrates were evaluated using a ball-on-plate sliding wear tester at 37°C in simulated body-fluid conditions. The microstructure of both the titanium alloy and coated specimen were examined using an optical microscope and scanning electron microscope. The hardness of the plasma-sprayed alumina-zirconia composite coatings was 2.5 times higher than that of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy, while the wear rate of Ti-6Al-4V alloy was 253 times higher than that of the composite-coated Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The superior wear resistance of the alumina-zirconia coated alloy is attributed to its enhanced hardness and intersplat bonding strength. Wear-track examination showed that the predominant wear mechanism of Ti-6Al-4V alloy was abrasive and adhesive wear, whereas, in the case of alumina-zirconia composite coated alloy, the wear was dominated by microchipping and microcracking.
Keywords: Hank’s solution; Ti-6Al-4V alloy; alumina–zirconia; titanium; wear.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Microstructure and mechanical properties of plasma sprayed HA/YSZ/Ti-6Al-4V composite coatings.Biomaterials. 2004 Aug;25(18):4009-17. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.10.089. Biomaterials. 2004. PMID: 15046891
-
Study on improved tribological properties by alloying copper to CP-Ti and Ti-6Al-4V alloy.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015 Dec 1;57:123-32. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.07.046. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015. PMID: 26354247
-
Studies on Mechanical, Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Activity of Plasma Sprayed Nano/Micron Ceramic Bilayered Coatings on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy for Biomedical Application.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018 Jul 1;18(7):4515-4523. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2018.15332. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29442627
-
Comparative analysis of corrosion resistance between beta titanium and Ti-6Al-4V alloys: A systematic review.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020 Dec;62:126618. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126618. Epub 2020 Jul 9. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32663743
-
Development of plasma-sprayed bioceramic coatings with bond coats based on titania and zirconia.Biomaterials. 1998 Aug;19(16):1507-11. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(98)00067-2. Biomaterials. 1998. PMID: 9794527 Review.
Cited by
-
New alternate bearing surfaces in total hip arthroplasty: A review of the current literature.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018 Jan-Mar;9(1):7-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2017.10.013. Epub 2017 Oct 27. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018. PMID: 29628677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface Modification Techniques of Titanium and its Alloys to Functionally Optimize Their Biomedical Properties: Thematic Review.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Nov 11;8:603072. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.603072. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33262980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The response of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells to micro- and nano-textured, hydrophilic and bioactive titanium surfaces.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016 Apr;27(4):68. doi: 10.1007/s10856-016-5678-5. Epub 2016 Feb 17. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016. PMID: 26886816
References
-
- Long M, Rack HJ. Titanium alloys in total joint replacement – a materials science perspective. Biomaterials. 1998;19(18):1621–1639. - PubMed
-
- Long M, Rack HJ. Friction and surface behavior of selected titanium alloys during reciprocating-sliding motion. Wear. 2001;249(1–2):158–168.
-
- Geetha M, Singh AK, Asokamani R, Gogia AK. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants – A review. Progr Mater Sci. 2009;54(3):397–425.
-
- Kustas FM, Misra B, Zhou Fabrication and characterization of TiB2/TiC and tungsten co-sputtered wear coatings. Surf Coat Technol. 2002;153(1):25–30.
-
- Blau HM, Brazelton TR, Weimann JM. The evolving concept of a stem cell: entity or function. Cell. 2001;105(7):829–841. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

