Anatomic and functional outcomes of retinectomy for the management of complicated retinal detachment with proliferative vitreoretinopathy
- PMID: 26491338
- PMCID: PMC4599044
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S89467
Anatomic and functional outcomes of retinectomy for the management of complicated retinal detachment with proliferative vitreoretinopathy
Abstract
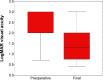
The aim of this study is to report the anatomic and functional outcomes of retinectomy for the management of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment complicated by proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR), comparing them with previously reported data and determining prognostic factors. Fifty-one eyes of 51 patients with established PVR grade C in which retinectomy was performed were retrospectively enrolled in the study. Primary outcome measures were anatomic success rate and final visual acuity. Secondary outcome measures were intraoperative complications, number of re-operations, and postoperative hypotony. Prognostic factors in relation to retinal re-attachment and final visual acuity were retrospectively analyzed. The rate of complete retinal re-attachment after one operation was 80% and after two operations it was 84%. At the end of the follow-up, the macula was attached in 96% of the cases. Mean LogMAR best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) improved significantly from 2.45±0.66 preoperatively to 1.37±0.75 at the end of the follow-up (P<0.001). BCVA improved in 37 eyes (72%), remained the same in eleven eyes (22%) and worsened in three eyes (6%). Postoperative hypotony was observed in 2% of cases. Postoperative BCVA was significantly correlated with preoperative BCVA (P<0.001), extension of PVR (P=0.013), preoperative use of gas instead of silicone oil (SO) (P=0.01), and removal of SO (P=0.05). SO was left in situ in 35% of eyes. In conclusion, retinectomy is a surgical option providing good anatomical and reasonable visual outcomes in complicated retinal detachment with PVR. Better preoperative visual acuity, lesser extension of PVR, and the use of gas tamponade during the primary repair are relevant factors for a successful outcome whereas re-proliferation of epiretinal membranes seems to be the main reason of anatomical failure.
Keywords: proliferative vitreoretinopathy; retinal detachment; retinectomy; vitrectomy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional outcome and prognostic factors in 304 eyes managed by retinectomy.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007 May;245(5):641-9. doi: 10.1007/s00417-006-0479-z. Epub 2006 Nov 22. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007. PMID: 17119994
-
Outcomes of vitrectomy with inferior retinectomy in patients with recurrent rhegmatogenous retinal detachments and proliferative vitreoretinopathy.Ophthalmology. 2006 Nov;113(11):2041-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.05.039. Epub 2006 Sep 6. Ophthalmology. 2006. PMID: 16952397
-
Outcomes of Retinectomy in Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2018 Nov;28(11):848-852. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2018.11.848. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2018. PMID: 30369377
-
Tamponade in surgery for retinal detachment associated with proliferative vitreoretinopathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 13;5(5):CD006126. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006126.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32408387 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting visual outcome following retinectomy for retinal detachment.Br J Ophthalmol. 2008 Jul;92(7):954-8. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2007.131540. Epub 2008 Jun 12. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 18556423 Review.
Cited by
-
Recurrent Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment: Characteristics, Risk Factors, and Outcomes.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2025 Apr 1;21:425-440. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S506037. eCollection 2025. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2025. PMID: 40191804 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes and predictors of vitrectomy and silicone oil tamponade in retinal detachments complicated by proliferative vitreoretinopathy.Int J Ophthalmol. 2022 Aug 18;15(8):1279-1289. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2022.08.09. eCollection 2022. Int J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36017034 Free PMC article.
-
Vitrectomy for Complicated Retinal Detachment Without the Use of Perfluorocarbon Liquid: A Real-World Data and Retrospective Study.Ophthalmol Ther. 2022 Apr;11(2):857-868. doi: 10.1007/s40123-022-00479-x. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Ophthalmol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35195877 Free PMC article.
-
Large Retinectomies for Retinal Detachment Complicated by Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy: Anatomical and Functional Outcome of Silicone Oil versus Perfluoropropane Gas.Clin Ophthalmol. 2020 Sep 15;14:2679-2686. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S241479. eCollection 2020. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32982160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Quiram PA, Gonzales CR, Hu W, et al. Outcomes of vitrectomy with inferior retinectomy in patients with recurrent rhegmatogenous retinal detachments and proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Ophthalmology. 2006;113(11):2041–2047. - PubMed
-
- Faude F, Lambert A, Wiedemann P. 360 degrees retinectomy in severe anterior PVR and PDR. Int Ophthalmol. 2004;22(2):119–123. - PubMed
-
- Morel C, Doan S, Rivoal O, Ameline B, Monin C, Larricart P. Relaxing retinopathies and liquid perfluorocarbons. J Fr Ophthalmol. 1998;21(5):315–320. - PubMed
-
- Metge F, Massin P, Gaudric A. Retinectomies in the treatment of retinal detachments with vitreoretinal proliferation. J Fr Ophthalmol. 1997;20(5):345–349. - PubMed
-
- Lu L, Gao R, Lin X. The application of retinotomy and retinectomy for complicated retinal detachment. Yan Ke Xue Bao. 1998;14(2):94–96. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials