Prognostic role of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in lung cancers: a meta-analysis including 7,054 patients
- PMID: 26491346
- PMCID: PMC4599071
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S90875
Prognostic role of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in lung cancers: a meta-analysis including 7,054 patients
Abstract
Background: Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has recently been reported to be a poor prognostic indicator in lung cancer. However, the prognostic value of the NLR in patients with lung cancer still remains controversial. We performed a meta-analysis to evaluate the prognostic value of NLR in patients with lung cancer.
Methods: We performed a comprehensive literature search in PubMed, Ovid, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases in May 2015. Studies were assessed for quality using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale.
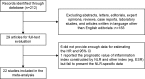
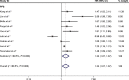
Results: Twenty-two studies with a total of 7,054 patients were included in this meta-analysis. The meta-analysis was performed to generate combined hazard ratios (HRs) for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). Our analysis results indicated that high NLR predicted poorer OS (HR, 1.51; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.33-1.71; P<0.001) and PFS (HR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.07-1.67; P=0.012) in patients with lung cancer. High NLR was also associated with poor OS in lung cancer treated by surgical resection (HR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.26-1.99; P<0.001) and chemotherapy (HR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.08-1.22; P<0.001). In addition, NLR cut-off value =5 (HR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.16-2.12; P=0.003) and NLR cut-off value <5 (HR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.28-1.69; P<0.001).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis result suggested that NLR should have significant predictive ability for estimating OS and PFS in patients with lung cancer and may be as a significant biomarker in the prognosis of lung cancer.
Keywords: NLR; lung cancer; meta-analysis; prognosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for predicting lung cancer prognosis: A meta-analysis of 7,219 patients.Mol Clin Oncol. 2017 Sep;7(3):498-506. doi: 10.3892/mco.2017.1342. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28811903 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Biomarker for Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 11;11:746976. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.746976. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34900692 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and clinical outcomes in patients with lung cancer receiving immunotherapy: a meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2020 Jun 3;10(6):e035031. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-035031. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32499266 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jul;96(29):e7577. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007577. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28723793 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Mar 7;21(9):2807-15. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2807. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25759553 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Albumin-to-fibrinogen ratio as a promising biomarker to predict clinical outcome of non-small cell lung cancer individuals.Cancer Med. 2018 Apr;7(4):1221-1231. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1428. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 29533009 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative change in neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a prognostic factor in patients with completely resected primary pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Mar;11(3):819-826. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.02.02. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31019770 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Parameter in NSCLC Patients Receiving EGFR-TKIs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Oncol. 2021 Jan 20;2021:6688346. doi: 10.1155/2021/6688346. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33542732 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Localized and Advanced Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 20;11(4):e0153981. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153981. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27096158 Free PMC article.
-
The postoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and changes in this ratio predict survival after the complete resection of stage I non-small cell lung cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Oct 21;9:6529-6537. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S117290. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27799800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5–29. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357(9255):539–545. - PubMed
-
- Grange JM, Krone B, Mastrangelo G. Infection, inflammation and cancer. Int J Cancer. 2011;128(9):2240–2241. - PubMed
-
- Moore MM, Chua W, Charles KA, Clarke SJ. Inflammation and cancer: causes and consequences. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010;87(4):504–508. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

