Advanced lung adenocarcinoma with spinal cord metastasis successfully treated with second EGFR-TKI treatment: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 26491347
- PMCID: PMC4599040
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S90213
Advanced lung adenocarcinoma with spinal cord metastasis successfully treated with second EGFR-TKI treatment: a case report and literature review
Abstract
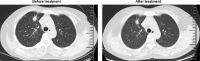
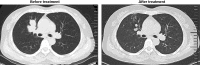
Lung adenocarcinoma can be accompanied by epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation. As a consequence, targeted therapy based on screening of tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs) is necessary. Spinal cord metastasis of lung cancer is a serious clinical problem. Here, we report a case of lung adenocarcinoma with severe spinal cord metastasis that was successfully treated with a second administration of an EGFR-TKI. Magnetic resonance imaging showed spinal cord metastasis to the cervical vertebrae. The patient received a second administration of an EGFR-TKI (150 mg/day erlotinib). Four months later, we observed the disappearance of the paravertebral tumor and a reduction in the size of pulmonary tumors in both lungs. These results indicate that EGFR-TKI therapy could be a new strategy for the treatment of advanced lung adenocarcinoma with spinal metastasis.
Keywords: NSCLC; compression of spinal cord; erlotinib; target therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heterogeneous resistance mechanisms in an EGFR exon 19-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patient treated with erlotinib: Persistent FGFR3-mutation, localized transformation to EGFR-mutated SCLC, and acquired T790M EGFR-mutation.Lung Cancer. 2017 Nov;113:14-17. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.08.024. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29110841
-
Overall survival and prognostic factors in patients with spinal metastases from lung cancer treated with and without epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Int J Clin Oncol. 2017 Aug;22(4):698-705. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1116-z. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Int J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28361340
-
Clinical impact of switching to a second EGFR-TKI after a severe AE related to a first EGFR-TKI in EGFR-mutated NSCLC.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012 Jun;42(6):528-33. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hys042. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22457323
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neoadjuvant and adjuvant epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) therapy for lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015 Feb;4(1):82-93. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2014.11.08. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25806348 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis and treatment of epidural metastases.Oncology (Williston Park). 1990 Apr;4(4):47-54; discussion 55, 58. Oncology (Williston Park). 1990. PMID: 2143929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful osimertinib treatment in a patient who exhibited intramedullary spinal cord metastases of lung adenocarcinoma with an acquired EGFR T790M mutation.BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Jun 21;12(6):e229310. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-229310. BMJ Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31229973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zeng Z, Chen HJ, Yan HH, Yang JJ, Zhang XC, Wu YL. Sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in males, smokers, and non-adenocarcinoma lung cancer in patients with EGFR mutations. Int J Biol Markers. 2013;28(3):249–258. - PubMed
-
- Cho BC, Im CK, Park MS, et al. Phase II study of erlotinib in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of gefitinib. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(18):2528–2533. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

