Fear of pain potentiates nocebo hyperalgesia
- PMID: 26491370
- PMCID: PMC4608595
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S91923
Fear of pain potentiates nocebo hyperalgesia
Abstract
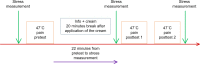
Nocebo hyperalgesia has received sparse experimental attention compared to placebo analgesia. The aim of the present study was to investigate if personality traits and fear of pain could predict experimental nocebo hyperalgesia. One hundred and eleven healthy volunteers (76 females) participated in an experimental study in which personality traits and fear of pain were measured prior to induction of thermal heat pain. Personality traits were measured by the Big-Five Inventory-10. Fear of pain was measured by the Fear of Pain Questionnaire III. Heat pain was induced by a PC-controlled thermode. Pain was measured by a computerized visual analog scale. Stress levels during the experiment were measured by numerical rating scales. The participants were randomized to a Nocebo group or to a no-treatment Natural History group. The results revealed that pain and stress levels were significantly higher in the Nocebo group after nocebo treatment. Mediation analysis showed that higher levels of the Fear of Pain Questionnaire III factor "fear of medical pain" significantly increased stress levels after nocebo treatment and that higher stress levels were associated with increased nocebo hyperalgesic responses. There were no significant associations between any of the personality factors and the nocebo hyperalgesic effect. The results from the present study suggest that dispositional fear of pain might be a useful predictor for nocebo hyperalgesia and emotional states concomitant with expectations of increased pain. Furthermore, measurement of traits that are specific to pain experience is probably better suited for prediction of nocebo hyperalgesic responses compared to broad measures of personality.
Keywords: emotions; fear of pain; five-factor model of personality; nocebo hyperalgesia; pain; personality.
Figures
References
-
- Enck P, Benedetti F, Schedlowski M. New insights into the placebo and nocebo responses. Neuron. 2008;59(2):195–206. - PubMed
-
- Colloca L, Benedetti F. Nocebo hyperalgesia: how anxiety is turned into pain. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2007;20(5):435–439. - PubMed
-
- Myers MG, Cairns JA, Singer J. The consent form as a possible cause of side effects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1987;42(3):250–253. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources